Efficacy and safety of ultra-long-acting insulin degludec
- PMID: 23148194
- PMCID: PMC3474648
- DOI: 10.1177/2042018812437181
Efficacy and safety of ultra-long-acting insulin degludec
Abstract
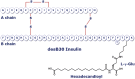
All patients with type 1 diabetes and significant numbers of those with type 2 diabetes are treated with insulin. Nonadherence to insulin regimen can impact glycaemic control. Insulin degludec is a new generation, ultra-long-acting basal insulin that forms soluble multihexamers at the injection site that slowly release insulin degludec monomers into the circulation giving a prolonged duration of action. Insulin degludec may provide a safe and convenient dosing option for patients who require some flexibility in adhering to an insulin regimen according to their lifestyle or circumstances. In this review we focus on the early phases of insulin degludec development.
Keywords: hypoglycaemia; insulin degludec; type 1 and type 2 diabetes; ultra-long-acting basal insulin.
Conflict of interest statement
Professor Atkin has undertaken consultancy and received research money from most large pharmaceutical companies.
Figures
References
-
- Atkin S.L., Bain S., Gough S., Shestakova M., Raz I., Blonde L., et al. (2011) Insulin degludec does not compromise efficacy or safety when given in a flexible once-daily dosing regimen compared to insulin glargine once daily at the same time each day in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 54 (Suppl. 1): 542
-
- Birkeland K.I., Raz I., Gough S., Atkin S.L., Shestakova M., Blonde L., et al. (2011b) Insulin degludec in a flexible daily dosing regimen provides similar glycaemic control without increasing rates of hypoglycaemia compared to dosing the same time daily in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 54 (Suppl. 1): S423 (1041-P).
-
- Donnelly L.A., Morris A.D., Evans J.M.M. for the DARTS/MEMO collaboration (2007) Adherence to insulin and its association with glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. QJM 100: 345–350 - PubMed
-
- Heise T., Hermanski L., Nosek L., Feldmann A., Rasmussen S., Stryhn T., et al. (2010) Insulin degludec: less pharmacodynamic variability than insulin glargine under steady state conditions. Diabetologia 53 (Suppl. 1): S 387 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources