IL-32 and IL-17 interact and have the potential to aggravate osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 23148681
- PMCID: PMC3674587
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4089
IL-32 and IL-17 interact and have the potential to aggravate osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Interleukin (IL)-32 and IL-17 play critical roles in pro-inflammatory responses and are highly expressed in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We investigated the relations between these two cytokines (IL-17 and IL-32) for their ability to induce each other and to stimulate osteoclasts in RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) and T cells.
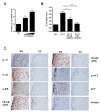
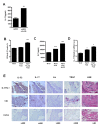
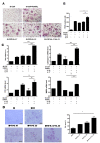
Methods: FLSs were isolated through surgical synovectomy obtained from patients with RA or osteoarthritis (OA). Real-time PCR were performed to evaluate the expression of IL-32, IL-17 and osteoclast-related genes. Immunohistochemical staining and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining were performed to determine the distribution of inflammatory cytokines and the presence of osteoclastogenesis.
Results: IL-17 induced the expression of IL-32 in the FLSs from RA patients, as assessed by microarray. IL-32 production was increased by IL-17. IL-32 in the FLSs from RA patients induced the production of IL-17 in CD4+ T cells. IL-32 and IL-17 were colocalized near TRAP-positive areas in joint specimens. IL-17 and IL-32 synergistically induced the differentiation of osteoclasts, as demonstrated by the expression of osteoclast-related genes. IL-32 and IL-17 also could induce resorption by osteoclasts in a RANKL-dependent manner.
Conclusions: IL-17 affected the expression of IL-32 in FLSs of RA patients and IL-32 induced the production of IL-17 in CD4+ T cells. Both IL-17 and IL-32 cytokines can reciprocally influence each other's production and amplify the function of osteoclastogenesis in the in RA synovium. Separately, IL-17 and IL-32 each stimulated osteoclastogenesis without RANKL. Together, the two cytokines synergistically amplified the differentiation of osteoclasts, independent of RANKL stimulation.
Figures


References
-
- Yamamura Y, Gupta R, Morita Y, He X, Pai R, Endres J, Freiberg A, Chung K, Fox DA. Effector function of resting T cells: activation of synovial fibroblasts. J Immunol. 2001;14:2270–2275. - PubMed
-
- Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S, Saito S, Inoue K, Kamatani N, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ, Suda T. IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1999;14:1345–1352. doi: 10.1172/JCI5703. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

