Airway obstruction and bronchodilator responsiveness in adults with acute cough
- PMID: 23149529
- PMCID: PMC3495926
- DOI: 10.1370/afm.1416
Airway obstruction and bronchodilator responsiveness in adults with acute cough
Abstract
Purpose: We sought to determine the prevalence of airway obstruction and bronchodilator responsiveness in adults consulting for acute cough in primary care.
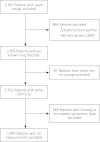
Methods: Family physicians recruited 3,105 adult patients with acute cough (28 days or shorter) attending primary care practices in 12 European countries. After exclusion of patients with preexisting physician-diagnosed asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), we undertook complete case analysis of spirometry results (n = 1,947) 28 to 35 days after inclusion. Bronchodilator responsiveness was diagnosed if there were recurrent complaints of wheezing, cough, or dyspnea and an increase of the forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV(1)) of 12% or more after bronchodilation. Airway obstruction was diagnosed according to 2 thresholds for the (postbronchodilator) ratio of FEV(1) to forced vital capacity (FEV(1):FVC): less than 0.7 and less than the lower limit of normal.
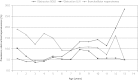
Results: There were 240 participants who showed bronchodilator responsiveness (12%), 193 (10%) had a FEV(1)/FVC ratio of less than 0.7, and 126 (6%) had a ratio of less than the lower limit of normal. Spearman's correlation between the 2 definitions of obstruction was 0.71 (P <.001), with discordance most pronounced among those younger than 30 years and in older participants.
Conclusions: Both bronchodilator responsiveness and persistent airway obstruction are common in adults without established asthma or COPD who consult for acute cough in primary care, which suggests a high risk of undiagnosed asthma and COPD. Different accepted methods to define airway obstruction detected different numbers of patients, especially at the extremes of age. As both conditions benefit from appropriate and timely interventions, clinicians should be aware and responsive to potential underdiagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: authors report none.
Figures
References
-
- Mannino DM, Homa DM, Akinbami LJ, Ford ES, Redd SC. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease surveillance—United States, 1971-2000. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2002;51(6):1-16 - PubMed
-
- Schappert SM, Burt CW. Ambulatory care visits to physician offices, hospital outpatient departments, and emergency departments: United States, 2001-02. Vital Health Stat 13. 2006;(159):1-66 - PubMed
-
- Rabe KF, Hurd S, Anzueto A, et al. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176(6):532-555 - PubMed
-
- From the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). 2012. http://www.ginasthma.org
