Hepatic Cyp2d and Cyp26a1 mRNAs and activities are increased during mouse pregnancy
- PMID: 23150428
- PMCID: PMC3558865
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.112.049379
Hepatic Cyp2d and Cyp26a1 mRNAs and activities are increased during mouse pregnancy
Abstract
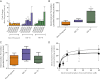
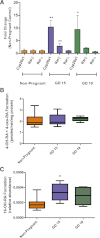
There is considerable evidence that drug disposition is altered during human pregnancy and based on probe drug studies, CYP2D6 activity increases during human pregnancy. The aim of this study was to determine whether the changes of CYP2D6 activity observed during human pregnancy could be replicated in the mouse, and explore possible mechanisms of increased CYP2D6 activity during pregnancy. Cyp2d11, Cyp2d22, Cyp2d26 and Cyp2d40 mRNA was increased (P < 0.05) on gestational days (GD) 15 and 19 compared with the non-pregnant controls. There was no change (P > 0.05) in Cyp2d9 and Cyp2d10 mRNA. In agreement with the increased Cyp2d mRNA, Cyp2d-mediated dextrorphan formation from dextromethorphan was increased 2.7-fold (P < 0.05) on GD19 (56.8±39.4 pmol/min/mg protein) when compared with the non-pregnant controls (20.8±11.2 pmol/min/mg protein). An increase in Cyp26a1 mRNA (10-fold) and retinoic acid receptor (Rar)β mRNA (2.8-fold) was also observed during pregnancy. The increase in Cyp26a1 and Rarβ mRNA during pregnancy indicates increased retinoic acid signaling in the liver during pregnancy. A putative retinoic acid response element was identified within the Cyp2d40 promoter and the mRNA of Cyp2d40 correlated (P < 0.05) with Cyp26a1 and Rarβ. These results show that Cyp2d mRNA is increased during mouse pregnancy the and mouse may provide a suitable model to investigate the mechanisms underlying the increased clearance of CYP2D6 probes observed during human pregnancy. Our findings also suggest that retinoic acid signaling in the liver is increased during pregnancy, which may have broader implications to energy homeostasis in the liver during pregnancy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Drug metabolism and transport during pregnancy: how does drug disposition change during pregnancy and what are the mechanisms that cause such changes?Drug Metab Dispos. 2013 Feb;41(2):256-62. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.050245. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013. PMID: 23328895 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α) in coordination with retinoic acid receptors increases all-trans-retinoic acid-dependent CYP26A1 gene expression in HepG2 human hepatocytes.J Cell Biochem. 2014 Oct;115(10):1740-51. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24839. J Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24819304 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of the roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor and retinoic acid receptor on CYP26 regulation.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Feb;77(2):218-27. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.059071. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19884280 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide opposes the induction of CYP26A1 and CYP26B1 gene expression by retinoic acid in the rat liver in vivo.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Apr;292(4):G1029-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00494.2006. Epub 2006 Dec 21. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17185629 Free PMC article.
-
Cytochrome P450s in the regulation of cellular retinoic acid metabolism.Annu Rev Nutr. 2011 Aug 21;31:65-87. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-072610-145127. Annu Rev Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21529158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comparison of Non-Human Primate Cytochrome P450 2D Members and the Implication in Drug Discovery.Curr Drug Metab. 2016;17(6):520-7. doi: 10.2174/1389200217666160219114241. Curr Drug Metab. 2016. PMID: 26892731 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered expression of small heterodimer partner governs cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 induction during pregnancy in CYP2D6-humanized mice.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 7;289(6):3105-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526798. Epub 2013 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24318876 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF) 4α transactivation of cytochrome P450 (Cyp) 2d40 promoter is enhanced during pregnancy in mice.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Mar 1;94(1):46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25598084 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of multiple CYP2D genes in mouse primary hepatocytes with a single siRNA construct.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015 Jan;51(1):9-14. doi: 10.1007/s11626-014-9803-9. Epub 2014 Aug 15. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015. PMID: 25124873 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of T helper cytokines in the liver during early pregnancy in sheep.Anim Reprod. 2019 Oct 23;16(2):332-339. doi: 10.21451/1984-3143-AR2018-0141. Anim Reprod. 2019. PMID: 33224295 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Pregnancy and Vitamin A Supplementation on CYP2D6 Activity.J Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Mar;63(3):363-372. doi: 10.1002/jcph.2169. Epub 2022 Nov 15. J Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36309846 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Anderson GD. (2005) Pregnancy-induced changes in pharmacokinetics: a mechanistic-based approach. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:989–1008 - PubMed
-
- Andrade SE, Gurwitz JH, Davis RL, Chan KA, Finkelstein JA, Fortman K, McPhillips H, Raebel MA, Roblin D, Smith DH, et al. (2004) Prescription drug use in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 191:398–407 - PubMed
-
- Cairns W, Smith CA, McLaren AW, Wolf CR. (1996) Characterization of the human cytochrome P4502D6 promoter. A potential role for antagonistic interactions between members of the nuclear receptor family. J Biol Chem 271:25269–25276 - PubMed
-
- Carcillo JA, Adedoyin A, Burckart GJ, Frye RF, Venkataramanan R, Knoll C, Thummel K, Roskos L, Wilson JW, Sereika S, et al. (2003) Coordinated intrahepatic and extrahepatic regulation of cytochrome p4502D6 in healthy subjects and in patients after liver transplantation. Clin Pharmacol Ther 73:456–467 - PubMed
-
- Chambon P. (1996) A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J 10:940–954 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

