Dynamic force sensing of filamin revealed in single-molecule experiments
- PMID: 23150587
- PMCID: PMC3511698
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1211274109
Dynamic force sensing of filamin revealed in single-molecule experiments
Abstract
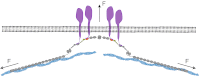
Mechanical forces are important signals for cell response and development, but detailed molecular mechanisms of force sensing are largely unexplored. The cytoskeletal protein filamin is a key connecting element between the cytoskeleton and transmembrane complexes such as integrins or the von Willebrand receptor glycoprotein Ib. Here, we show using single-molecule mechanical measurements that the recently reported Ig domain pair 20-21 of human filamin A acts as an autoinhibited force-activatable mechanosensor. We developed a mechanical single-molecule competition assay that allows online observation of binding events of target peptides in solution to the strained domain pair. We find that filamin force sensing is a highly dynamic process occurring in rapid equilibrium that increases the affinity to the target peptides by up to a factor of 17 between 2 and 5 pN. The equilibrium mechanism we find here can offer a general scheme for cellular force sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

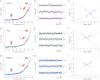

 in the black and gray traces are interrupted by low-SD regions with lifetimes
in the black and gray traces are interrupted by low-SD regions with lifetimes  . (B) A zoom into the blue region shows the transition between a high-SD (rapid opening and closing cycles of the tethered construct) and low-SD region (blocked fluctuations due to competitive peptide binding from solution). (C) Dependence of the bound and unbound lifetimes as a function of applied force and solution concentration. As expected for binding from solution,
. (B) A zoom into the blue region shows the transition between a high-SD (rapid opening and closing cycles of the tethered construct) and low-SD region (blocked fluctuations due to competitive peptide binding from solution). (C) Dependence of the bound and unbound lifetimes as a function of applied force and solution concentration. As expected for binding from solution,  depends on the opening probability of the tethered construct and hence the applied force, as well as the solution concentration, whereas
depends on the opening probability of the tethered construct and hence the applied force, as well as the solution concentration, whereas  is independent (see text and
is independent (see text and 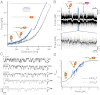
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

