Activation of liver X receptor induces macrophage interleukin-5 expression
- PMID: 23150660
- PMCID: PMC3527921
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.403394
Activation of liver X receptor induces macrophage interleukin-5 expression
Abstract
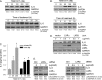
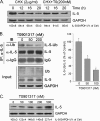
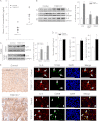
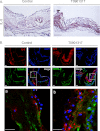
IL-5 stimulates production of T15/EO6 IgM antibodies that can block the uptake of oxidized low density lipoprotein by macrophages, whereas a deficiency in macrophage IL-5 expression accelerates development of atherosclerosis. Liver X receptors (LXRs) are ligand-activated transcription factors that can induce macrophage ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux, thereby inhibiting the development of atherosclerosis. However, it remains unknown whether additional mechanisms, such as the regulation of macrophage IL-5 expression, are related to the anti-atherogenic properties of LXR. We initially defined IL-5 expression in macrophages where the LXR ligand (T0901317) induced macrophage IL-5 protein expression and secretion. The overexpression of LXR increased, whereas its knockdown inhibited IL-5 expression. Furthermore, we found that LXR activation increased IL-5 transcripts, promoter activity, formation of an LXR·LXR-responsive element complex, and IL-5 protein stability. In vivo, we found that T0901317 increased IL-5 and total IgM levels in plasma and IL-5 expression in multiple tissues in wild type mice. In LDL receptor knock-out (LDLR(-/-)) mice, T0901317 increased IL-5 expression in the aortic root area. Taken together, our studies demonstrate that macrophage IL-5 is a target gene for LXR activation, and the induction of macrophage IL-5 expression can be related to LXR-inhibited atherosclerosis.
Figures


References
-
- Mitra S., Deshmukh A., Sachdeva R., Lu J., Mehta J. L. (2011) Oxidized low-density lipoprotein and atherosclerosis implications in antioxidant therapy. Am. J. Med. Sci. 342, 135–142 - PubMed
-
- Esterbauer H., Schaur R. J., Zollner H. (1991) Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 11, 81–128 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

