Palm tocotrienol supplementation enhanced bone formation in oestrogen-deficient rats
- PMID: 23150728
- PMCID: PMC3485551
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/532862
Palm tocotrienol supplementation enhanced bone formation in oestrogen-deficient rats
Abstract
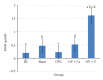
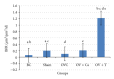
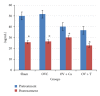
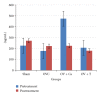
Postmenopausal osteoporosis is the commonest cause of osteoporosis. It is associated with increased free radical activity induced by the oestrogen-deficient state. Therefore, supplementation with palm-oil-derived tocotrienols, a potent antioxidant, should be able to prevent this bone loss. Our earlier studies have shown that tocotrienol was able to prevent and even reverse osteoporosis due to various factors, including oestrogen deficiency. In this study we compared the effects of supplementation with palm tocotrienol mixture or calcium on bone biomarkers and bone formation rate in ovariectomised (oestrogen-deficient) female rats. Our results showed that palm tocotrienols significantly increased bone formation in oestrogen-deficient rats, seen by increased double-labeled surface (dLS/Bs), reduced single-labeled surface (sLS/BS), increased mineralizing surface (MS/BS), increased mineral apposition rate (MAR), and an overall increase in bone formation rate (BFR/BS). These effects were not seen in the group supplemented with calcium. However, no significant changes were seen in the serum levels of the bone biomarkers, osteocalcin, and cross-linked C-telopeptide of type I collagen, CTX. In conclusion, palm tocotrienol is more effective than calcium in preventing oestrogen-deficient bone loss. Further studies are needed to determine the potential of tocotrienol as an antiosteoporotic agent.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of annatto-derived tocotrienol supplementation on osteoporosis induced by testosterone deficiency in rats.Clin Interv Aging. 2014 Aug 5;9:1247-59. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S67016. eCollection 2014. Clin Interv Aging. 2014. PMID: 25120355 Free PMC article.
-
Tocotrienol offers better protection than tocopherol from free radical-induced damage of rat bone.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005 Sep;32(9):761-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2005.04264.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16173934
-
Tocotrienol supplementation in postmenopausal osteoporosis: evidence from a laboratory study.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2013 Oct;68(10):1338-43. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2013(10)08. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2013. PMID: 24212841 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Neuroprotective Efficacy of Palm Oil and Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction from Palm Oil: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2020 Feb 18;12(2):521. doi: 10.3390/nu12020521. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32085610 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Tocotrienol in Preventing Male Osteoporosis-A Review of Current Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 18;20(6):1355. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061355. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30889819 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Effects of Selected Botanical Agents on Bone.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 May 11;15(5):963. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15050963. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29751644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventative and therapeutic potential of tocotrienols on musculoskeletal diseases in ageing.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 11;14:1290721. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1290721. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38146461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Vitamin E from Elaeis guineensis (Oil Palm) in a Rat Model of Bone Loss Due to Metabolic Syndrome.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Aug 24;15(9):1828. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15091828. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30149518 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of annatto-derived tocotrienol supplementation on osteoporosis induced by testosterone deficiency in rats.Clin Interv Aging. 2014 Aug 5;9:1247-59. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S67016. eCollection 2014. Clin Interv Aging. 2014. PMID: 25120355 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Obesity and Metabolic Complications by Gamma and Delta Tocotrienols.Molecules. 2016 Mar 11;21(3):344. doi: 10.3390/molecules21030344. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 26978344 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muthusami S, Ramachandran I, Muthusamy B, et al. Ovariectomy induces oxidative stress and impairs bone antioxidant system in adult rats. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2005;360(1-2):81–86. - PubMed
-
- Lean JM, Jagger CJ, Kirstein B, Fuller K, Chambers TJ. Hydrogen peroxide is essential for estrogen-deficiency bone loss and osteoclast formation. Endocrinology. 2005;146(2):728–735. - PubMed
-
- Altindag O, Erel O, Soran N, Celik H, Selek S. Total oxidative/anti-oxidative status and relation to bone mineral density in osteoporosis. Rheumatology International. 2008;28(4):317–321. - PubMed
-
- Nazrun AS, Luke DA, Khalid BAK, Ima-Nirwana S. Vitamin E protects from free-radical damage on femur of rats treated with ferric nitrilotriacetate. Current Topics in Pharmacology. 2005;9(2):107–115.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

