A novel role for lipid droplets in the organismal antibacterial response
- PMID: 23150794
- PMCID: PMC3491588
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.00003
A novel role for lipid droplets in the organismal antibacterial response
Abstract
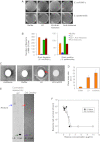
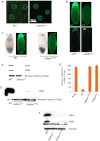
We previously discovered histones bound to cytosolic lipid droplets (LDs); here we show that this forms a cellular antibacterial defense system. Sequestered on droplets under normal conditions, in the presence of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or lipoteichoic acid (LTA), histones are released from the droplets and kill bacteria efficiently in vitro. Droplet-bound histones also function in vivo: when injected into Drosophila embryos lacking droplet-bound histones, bacteria grow rapidly. In contrast, bacteria injected into embryos with droplet-bound histones die. Embryos with droplet-bound histones displayed more than a fourfold survival advantage when challenged with four different bacterial species. Our data suggests that this intracellular antibacterial defense system may function in adult flies, and also potentially in mice.DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00003.001.
Keywords: B. subtilis; D. melanogaster; E. coli; Mouse; anti-bacterial; histones; innate immunity; lipid droplet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures







Comment in
-
Histones join the fight against bacteria inside cells.Elife. 2012 Nov 13;1:e00302. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00302. Elife. 2012. PMID: 23150800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augusto LA, Decottignies P, Synguelakis M, Nicaise M, Le Maréchal P, Chaby R. 2003. Histones: a novel class of lipopolysaccharide-binding molecules. Biochemistry 42:3929–38 - PubMed
-
- Bielecki J, Youngman P, Connelly P, Portnoy DA. 1990. Bacillus subtilis expressing a haemolysin gene from Listeria monocytogenes can grow in mammalian cells. Nature 345:175–6 - PubMed
-
- Bliska JB, Casadevall A. 2009. Intracellular pathogenic bacteria and fungi—a case of convergent evolution? Nat Rev Microbiol 7:165–71 - PubMed
-
- Bolton SJ, Perry VH. 1997. Histone H1; a neuronal protein that binds bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Neurocytol 26:823–31 - PubMed
-
- Bozza PT, Viola JP. 2010. Lipid droplets in inflammation and cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 82:243–50 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

