Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus
- PMID: 23150796
- PMCID: PMC3485615
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.00049
Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus
Erratum in
- Elife. 2014;3:e05570
Abstract
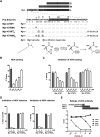
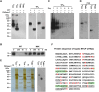
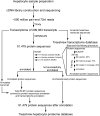
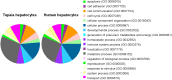
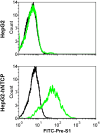
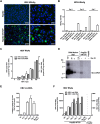
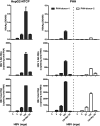
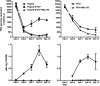
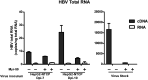
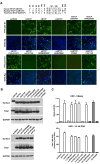
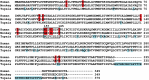
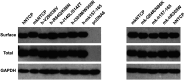
Human hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and HBV-related diseases remain a major public health problem. Individuals coinfected with its satellite hepatitis D virus (HDV) have more severe disease. Cellular entry of both viruses is mediated by HBV envelope proteins. The pre-S1 domain of the large envelope protein is a key determinant for receptor(s) binding. However, the identity of the receptor(s) is unknown. Here, by using near zero distance photo-cross-linking and tandem affinity purification, we revealed that the receptor-binding region of pre-S1 specifically interacts with sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP), a multiple transmembrane transporter predominantly expressed in the liver. Silencing NTCP inhibited HBV and HDV infection, while exogenous NTCP expression rendered nonsusceptible hepatocarcinoma cells susceptible to these viral infections. Moreover, replacing amino acids 157-165 of nonfunctional monkey NTCP with the human counterpart conferred its ability in supporting both viral infections. Our results demonstrate that NTCP is a functional receptor for HBV and HDV.DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00049.001.
Keywords: Other; Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; Viruses; hepatitis B virus; hepatitis D virus; liver; receptor; virus infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



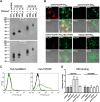
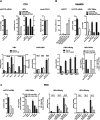
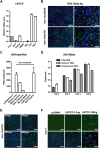
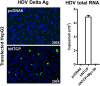



Comment in
-
Getting to grips with hepatitis.Elife. 2012 Nov 13;1:e00301. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00301. Elife. 2012. PMID: 23150799 Free PMC article.
-
A bile acid transporter as a candidate receptor for hepatitis B and D virus entry.J Hepatol. 2013 Jun;58(6):1246-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.01.036. Epub 2013 Feb 8. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23453223 No abstract available.
References
-
- Boehm ST, Thasler WE, Weiss TS, Jilg W. Primary human hepatocytes as an in vitro model for hepatitis B virus infection. In: Von Weizsäcker F, Roggendorf M, editors. Models of viral hepatitis. Vol 25. Basel: Karger; 2005. pp. 119–134.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

