Mitochondrial Pathway of α-Tocopheryl Succinate-Induced Apoptosis in Human Epidermoid Carcinoma A431 Cells
- PMID: 23150807
- PMCID: PMC3491895
Mitochondrial Pathway of α-Tocopheryl Succinate-Induced Apoptosis in Human Epidermoid Carcinoma A431 Cells
Abstract
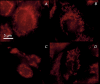
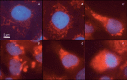
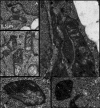
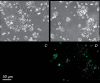
Vitamin E derivatives are known to act as agents exhibiting cytotoxity against tumor cells. The effect of vitamin E succinate on human epidermoid carcinoma cell line A431 was investigated in this study using live imaging, immunocytochemistry, and transmission electron microscopy. α-Tocopheryl succinate-induced apoptotic cell death in A431 cells was shown to be both dose- and time-dependent. The hyperproduction of reactive oxygen species, changes in size, shape and ultrastructural characteristics of mitochondria followed by the release of cytochromecfrom mitochondria to cytosol were observed. These results suggest that α-tocopheryl succinate induces apoptosis that occurs via the mitochondrial pathway. Mitochondria are shown to be crucial targets in α-tocopheryl succinate-induced caspase-dependent cell death in human carcinoma A431 cells.
Keywords: ROS; apoptosis; cytochromec; mitochondrial pathway; α-tocopheryl succinate.
Figures



References
-
- Prasad K.N., Edwards-Prasad J.. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1992;11:487–500. - PubMed
-
- Kelloff G.J., Crowell J.A., Boone C.W., Steele V.E., Lubet R.A., Greenwald P., Alberts D.S., Covey J.M., Doody L.A., Knapp G.G.. J. Cell Biochem. Suppl. 1994;20:282–299. - PubMed
-
- Theriault R.L., Lipton A., Hortobagyi G.N., Leff R., Gluck S., Stewart J.F., Costello S., Seaman J.J.. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999;17:846–854. - PubMed
-
- Fariss M.W., Fortuna M.B., Everett C.K., Smith J.D., Trent D.F., Djuric Z.. Cancer Res. 1994;54:3346–3351. - PubMed
-
- Kline K., Yu W., Sanders B.G.. Mol Carcinog. 1998;22(4):247–257. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
