TGF beta1 and related-Smads contribute to pulmonary metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice model
- PMID: 23151305
- PMCID: PMC3503772
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-31-93
TGF beta1 and related-Smads contribute to pulmonary metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice model
Abstract
Background: Recent studies indicate that Transforming Growth Factor beta (TGF β) correlated with pulmonary metastasis of cancers. However, the correlation between TGF β and pulmonary metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is till unknown.
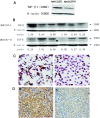
Methods: We detected the in vitro and in vivo expression levels of TGF β1/Smads by Real-time PCR and Western blot in MHCC97-H and MHCC97-L cell lines, which are HCC cell lines and have higher and lower pulmonary metastatic potential respectively.
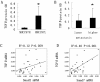
Results: TGF β1 mRNA level in MHCC97-L tumors were higher than that in MHCC97-H tumors, (2.81±1.61 vs. 1.24±0.96, P=0.002), TGF β1 protein level in MHCC97-L tumors were also higher than that in MHCC97-H tumors (1.37±0.95 vs. 0.32±0.22, P<0.001). In addition, the TGF β1 mRNA level positively correlated with pulmonary metastasis, and the relations between TGF β1 and Smads were also found (R2=0.12 and 0.40, respectively).
Conclusions: Our results suggest that TGF β/ Smads promote pulmonary metastasis of HCC.
Figures

References
-
- Ono T, Yamanoi A, Nazmy E, Assal O, Kohno H, Nagasue N. Adjuvant chemotherapy after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma causes deterioration of long-term prognosis in cirrhotic patients: meta analysis of three randomized controlled trials. Cancer. 2001;91:2378–2385. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(20010615)91:12<2378::AID-CNCR1271>3.0.CO;2-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

