MRI perfusion in determining pseudoprogression in patients with glioblastoma
- PMID: 23151413
- PMCID: PMC4755513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2012.02.016
MRI perfusion in determining pseudoprogression in patients with glioblastoma
Abstract
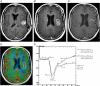
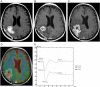
We examine the role of dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) perfusion in differentiating pseudoprogression from progression in 20 consecutive patients with treated glioblastoma. MRI perfusion was performed, and relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV), relative peak height (rPH), and percent signal recovery (PSR) were measured. Pseudoprogression demonstrated lower median rCBV (P=.009) and rPH (P<.001), and higher PSR (P=.039) than progression. DSC MRI perfusion successfully identified pseudoprogression in patients who did not require a change in treatment despite radiographic worsening following chemoradiotherapy.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC, Cairncross JG. Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8(7):1277–80. - PubMed
-
- Brandsma D, Stalpers L, Taal W, Sminia P, van den Bent MJ. Clinical features, mechanisms, and management of pseudoprogression in malignant gliomas. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9(5):453–61. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlain MC, Glantz MJ, Chalmers L, Van Horn A, Sloan AE. Early necrosis following concurrent Temodar and radiotherapy in patients with glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 2007;82(1):81–3. - PubMed
-
- Brandes AA, Franceschi E, Tosoni A, et al. MGMT promoter methylation status can predict the incidence and outcome of pseudoprogression after concomitant radiochemotherapy in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(13):2192–7. - PubMed
-
- Chaskis C, Neyns B, Michotte A, De Ridder M, Everaert H. Pseudoprogression after radiotherapy with concurrent temozolomide for high-grade glioma: clinical observations and working recommendations. Surg Neurol. 2009;72(4):423–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

