G9a functions as a molecular scaffold for assembly of transcriptional coactivators on a subset of glucocorticoid receptor target genes
- PMID: 23151507
- PMCID: PMC3511704
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1211803109
G9a functions as a molecular scaffold for assembly of transcriptional coactivators on a subset of glucocorticoid receptor target genes
Abstract
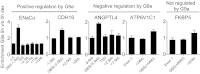
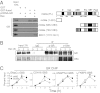
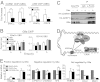
Histone H3 lysine-9 methyltransferase G9a/EHMT2/KMT1C is a key corepressor of gene expression. However, activation of a limited number of genes by G9a (independent of its catalytic activity) has also been observed, although the precise molecular mechanisms are unknown. By using RNAi in combination with gene expression microarray analysis, we found that G9a functions as a positive and a negative transcriptional coregulator for discrete subsets of genes that are regulated by the hormone-activated Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR). G9a was recruited to GR-binding sites (but not to the gene body) of its target genes and interacted with GR, suggesting recruitment of G9a by GR. In contrast to its corepressor function, positive regulation of gene expression by G9a involved G9a-mediated enhanced recruitment of coactivators CARM1 and p300 to GR target genes. Further supporting a role for G9a as a molecular scaffold for its coactivator function, the G9a-specific methyltransferase inhibitor UNC0646 did not affect G9a coactivator function but selectively decreased G9a corepressor function for endogenous target genes. Overall, G9a functioned as a coactivator for hormone-activated genes and as a corepressor in support of hormone-induced gene repression, suggesting that the positive or negative actions of G9a are determined by the gene-specific regulatory environment and chromatin architecture. These findings indicate distinct mechanisms of G9a coactivator vs. corepressor functions in transcriptional regulation and provide insight into the molecular mechanisms of G9a coactivator function. Our results also suggest a physiological role of G9a in fine tuning the set of genes that respond to glucocorticoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A distinct mechanism for coactivator versus corepressor function by histone methyltransferase G9a in transcriptional regulation.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 9;286(49):41963-41971. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.298463. Epub 2011 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21984853 Free PMC article.
-
A post-translational modification switch controls coactivator function of histone methyltransferases G9a and GLP.EMBO Rep. 2017 Aug;18(8):1442-1459. doi: 10.15252/embr.201744060. Epub 2017 Jun 14. EMBO Rep. 2017. PMID: 28615290 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H3 lysine 9 methyltransferase G9a is a transcriptional coactivator for nuclear receptors.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 31;281(13):8476-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511093200. Epub 2006 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16461774 Free PMC article.
-
Novel glucocorticoid receptor coactivator effector mechanisms.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001 Apr;12(3):122-6. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(00)00357-x. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001. PMID: 11306337 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid-Regulated Gene Transcription.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;872:59-81. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2895-8_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26215990 Review.
Cited by
-
The histone H3K9 methyltransferase G9a regulates tendon formation during development.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 5;14(1):20771. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71570-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39237663 Free PMC article.
-
Different chromatin and DNA sequence characteristics define glucocorticoid receptor binding sites that are blocked or not blocked by coregulator Hic-5.PLoS One. 2018 May 8;13(5):e0196965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196965. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29738565 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct, genome-wide, gene-specific selectivity patterns of four glucocorticoid receptor coregulators.Nucl Recept Signal. 2014 Nov 4;12:e002. doi: 10.1621/nrs.12002. eCollection 2014. Nucl Recept Signal. 2014. PMID: 25422592 Free PMC article.
-
SETDB1 accelerates tumourigenesis by regulating the WNT signalling pathway.J Pathol. 2015 Mar;235(4):559-70. doi: 10.1002/path.4482. Epub 2014 Dec 18. J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25404354 Free PMC article.
-
G9a-mediated methylation of ERα links the PHF20/MOF histone acetyltransferase complex to hormonal gene expression.Nat Commun. 2016 Mar 10;7:10810. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10810. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26960573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tachibana M, Sugimoto K, Fukushima T, Shinkai Y. Set domain-containing protein, G9a, is a novel lysine-preferring mammalian histone methyltransferase with hyperactivity and specific selectivity to lysines 9 and 27 of histone H3. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(27):25309–25317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

