Supplementation with 1000 IU vitamin D/d leads to parathyroid hormone suppression, but not increased fractional calcium absorption, in 4-8-y-old children: a double-blind randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 23151536
- PMCID: PMC3522137
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.112.046102
Supplementation with 1000 IU vitamin D/d leads to parathyroid hormone suppression, but not increased fractional calcium absorption, in 4-8-y-old children: a double-blind randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The effects of vitamin D supplementation in healthy prepubertal children on physiologic outcomes have not been investigated.
Objective: The objective was to evaluate the effects of supplementation with 1000 IU vitamin D(3)/d on calcium absorption.
Design: In a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, we randomly assigned 64 children to 1000 IU vitamin D(3)/d (n = 32) or placebo (n = 32) for 8 wk. Stable isotopes were used to assess calcium absorption. The main outcome measure was calcium absorption before and after supplementation.
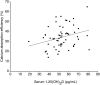
Results: All of the data are shown as means ± SDs. At baseline, vitamin D intake was 221 ± 79 IU/d and calcium intake was 830 ± 197 mg/d. Baseline serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] was not significantly correlated with fractional or total calcium absorption. After 8 wk, with baseline values used as a covariate, no differences were seen in fractional or total calcium absorption based on supplementation group (P = 0.75 and 0.36, respectively). Supplemented children had a significant increase in 25(OH)D concentrations (from 27.7 ± 7.4 to 36.0 ± 10.3 ng/mL; P < 0.0001) and a decrease in parathyroid hormone (from 21.4 ± 10.4 to 12.9 ± 7.1 pg/mL; P < 0.001); no significant changes in the placebo group were observed. No adverse side effects were noted in either group.
Conclusions: Vitamin D(3) supplementation at 1000 IU/d increases 25(OH)D and decreases parathyroid hormone in children with average vitamin D intakes below the dietary recommendations of the Institute of Medicine. However, no significant effects of this change on calcium absorption occurred. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT 00868738.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00868738.
Figures

References
-
- Institute of Medicine Dietary Reference Intakes for calcium and vitamin D. Washington, DC: National Academies Press, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, Murad MH, Weaver CM. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:1911–30 - PubMed
-
- Vieth R, Bischoff-Ferrari H, Boucher BJ, Dawson-Hughes B, Garland CF, Heaney RP, Holick MF, Hollis BW, Lamberg-Allardt C, McGrath JJ, et al. The urgent need to recommend an intake of vitamin D that is effective. Am J Clin Nutr 2007;85:649–50 - PubMed
-
- Hollis BW. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels indicative of vitamin D sufficiency: implications for establishing a new effective dietary intake recommendation for vitamin D. J Nutr 2005;135:317–22 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

