Information provision for stroke patients and their caregivers
- PMID: 23152210
- PMCID: PMC6544775
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001919.pub3
Information provision for stroke patients and their caregivers
Update in
-
Information provision for stroke survivors and their carers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 23;11(11):CD001919. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001919.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34813082 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Research shows that stroke patients and their families are dissatisfied with the information provided and have a poor understanding of stroke and associated issues.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of information provision strategies in improving the outcome for stroke patients or their identified caregivers, or both.
Search methods: For this update we searched the Cochrane Stroke Group Trials Register (June 2012), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled trials (CENTRAL), the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), the Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE), the NHS Economic Evaluation Database (EED), and the Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Database (The Cochrane Library June, 2012), MEDLINE (1966 to June 2012), EMBASE (1980 to June 2012), CINAHL (1982 to June 2012) and PsycINFO (1974 to June 2012). We also searched ongoing trials registers, scanned bibliographies of relevant articles and books and contacted researchers.
Selection criteria: Randomised trials involving patients or carers of patients with a clinical diagnosis of stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA) where an information intervention was compared with standard care, or where information and another therapy were compared with the other therapy alone.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trial eligibility and methodological quality and extracted data. Primary outcomes were knowledge about stroke and stroke services, and impact on mood.
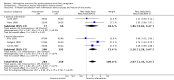
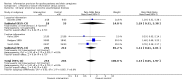
Main results: We have added four new trials to this update. This review now includes 21 trials involving 2289 patient and 1290 carer participants. Nine trials evaluated a passive and 12 trials an active information intervention. Meta-analyses showed a significant effect in favour of the intervention on patient knowledge (standardised mean difference (SMD) 0.29, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.12 to 0.46, P < 0.001), carer knowledge (SMD 0.74, 95% CI 0.06 to 1.43, P = 0.03), one aspect of patient satisfaction (odds ratio (OR) 2.07, 95% CI 1.33 to 3.23, P = 0.001), and patient depression scores (mean difference (MD) -0.52, 95% CI -0.93 to -0.10, P = 0.01). There was no significant effect (P > 0.05) on number of cases of anxiety or depression in patients, carer mood or satisfaction, or death. Qualitative analyses found no strong evidence of an effect on other outcomes. Post-hoc subgroup analyses showed that active information had a significantly greater effect than passive information on patient mood but not on other outcomes.
Authors' conclusions: There is evidence that information improves patient and carer knowledge of stroke, aspects of patient satisfaction, and reduces patient depression scores. However, the reduction in depression scores was small and may not be clinically significant. Although the best way to provide information is still unclear there is some evidence that strategies that actively involve patients and carers and include planned follow-up for clarification and reinforcement have a greater effect on patient mood.
Conflict of interest statement
John Young, Jane Smith and Anne Forster have conducted a randomised trial evaluating an education programme for patients and carers after stroke. The trial is included in this review (Smith 2004).
Figures










Update of
-
Information provision for stroke patients and their caregivers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Apr 16;(2):CD001919. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001919.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11:CD001919. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001919.pub3. PMID: 18425877 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Banet 1997 {published data only}
-
- Banet GA, Felchlia MA. The potential utility of a shared medical record in a "first‐time" stroke population. Journal of Vascular Nursing 1997;15(1):29‐33. - PubMed
Chinchai 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chinchai P, Bunyamark T, Sirisatayawong P. Effects of caregiver education in stroke rehabilitation on the quality of life of stroke survivors. World Federation of Occupational Therapists Bulletin 2010;61:56‐63.
Chiu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Chiu C‐C, Wu S‐S, Lee P‐Y, Huang Y‐C, Tan T‐Y, Chang K‐C. Control of modifiable risk factors in ischemic stroke outpatients by pharmacist intervention: an equal allocation stratified randomized study. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 2008;33(5):529‐35. - PubMed
Downes 1993 {unpublished data only}
-
- Downes B, Rooney V, Roper‐Hall A, Oyebode J, Main A, Mayer P. The effectiveness of counselling stroke survivors and their carers in the community. Age and Ageing 1993;22 Suppl 3:28.
-
- Downes B, Rooney V, Roper‐Hall A, Oyebode J, Mayer P, Main A. The effect of giving information and counselling on depression and anxiety in stroke survivors and carers (The Birmingham Stroke Counselling Project). Unpublished.
Draper 2007 {published data only}
-
- Draper B, Bowring G, Thompson C, Heyst J, Conroy P, Thompson J. Stress in caregivers of aphasic stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2007;21:122‐30. - PubMed
Ellis 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ellis G, Rodger J, McAlpine C, Langhorne P. The impact of stroke nurse specialist input on risk factor modification: a randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2005;34(4):389‐92. - PubMed
Evans 1988 {published data only}
-
- Evans RL, Matlock AL, Bishop DS, Stranahan S, Pederson C. Family intervention after stroke: does counselling or education help?. Stroke 1988;19:1243‐9. - PubMed
Frank 2000 {published data only}
-
- Frank G. Evaluation of a workbook‐based intervention for stroke patients. Diplomarbeit, Psychologisches Institut der Universitaet Tuebingen 1997.
-
- Frank G, Johnston M, Morrison V, Pollard B, MacWalter R. Perceived control and recovery from functional limitations: preliminary evaluation of a workbook‐based intervention for discharged stroke patients. British Journal of Health Psychology 2000;5:413‐20.
Hoffmann 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hoffmann T, McKenna K, Worrall L, Read S. Randomised trial of a computer‐generated tailored written education package for patients following stroke. Age and Ageing 2007;36:280‐6. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann T, Russell T, McKenna K. Producing computer‐generated tailored written information for stroke patients and their carers: system development and preliminary evaluation. International Journal of Medical Informatics 2004;73:751‐8. - PubMed
Johnson 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Johnson J, Pearson V. The effects of a structured education course on stroke survivors living in the community. Rehabilitation Nursing 2000;25(2):59‐65.
-
- Johnson J, Pearson V, McDivitt L. Stroke rehabilitation: assessing stroke survivors' long‐term learning needs. Rehabilitation Nursing 1997;22(5):243‐8. - PubMed
-
- Pearson V, Johnson J. Educational intervention reduces occurrence of depression in community‐dwelling stroke survivors. Stroke 2005;36(2):423.
Johnston 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Johnston M, Bonetti D, Joice S, Pollard B, Morrison V, Francis J, et al. Recovery from disability after stroke as a target for a behavioural intervention: results of a randomized controlled trial. Disability and Rehabilitation 2007;29(14):1117‐27. - PubMed
Kalra 2004 {published and unpublished data}
Larson 2005 {published data only}
-
- Larson J, Franzen‐Dahlin A, Billing E, Arbin M, Murray V, Wredling R. The impact of a nurse‐led support and education programme for spouses of stroke patients: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2005;14:995‐1003. - PubMed
Lomer 1987 {published data only}
-
- Lomer M, McLellan DL. Informing hospital patients and their relatives about stroke. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 1986;9(1):103‐4.
-
- Lomer M, McLellen DL. Informing hospital patients and their relatives about stroke. Clinical Rehabilitation 1987;1:33‐7.
Lowe 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lowe D, Leathley M, Sharma AK. An assessment of the utility of an individualised information booklet in patients after stroke. Age and Ageing 2005;34 Suppl 1:i38. - PubMed
-
- Lowe D, Leathley M, Sharma AK. Assessment of stroke knowledge. Age and Ageing 2002;31 Suppl 1:42.
-
- Lowe D, Leathley M, Sharma AK. Patient education following stroke: the CareFile Project. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2002;13 Suppl 3:81.
-
- Lowe D, Leathley M, Sharma AK. The effects of an individualised information booklet in post‐stroke patients: the CareFile Project. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2003;14 Suppl 4:95.
-
- Lowe D, Sharma A, Leathley M. The CareFile project: a feasibility study to examine the effects of an individualised information booklet on patients after stroke. Age and Ageing 2007; Vol. 36:83‐9. - PubMed
Maasland 2007 {published data only}
-
- Maasland E, Koudstaal PJ, Habbema JDF, Dippel DWJ. Effects of an individualised multimedia computer programme for health education in patients with a recent minor stroke or transient ischemic attack ‐ a randomized controlled trial. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2007;115:41‐8. - PubMed
Mant 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mant J, Carter J, Wade DT, Winner S. The impact of an information pack on patients with stroke and their carers: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 1998;12:465‐76. - PubMed
O'Connell 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- O'Connell B, Hawkins M, Botti M, Buchbinder R, Baker L. Providing information to stroke survivors: lessons from a failed randomised controlled trial. Journal of the Australasian Rehabilitation Nurses' Association 2009;12:4‐6.
Pain 1990 {published data only}
-
- Pain HSB, McLellan DL. The use of individualised booklets after a stroke. Clinical Rehabilitation 1990;4:265‐72.
Rodgers 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Atkinson C, Curless RH, Bond S, Suddes M, Dobson R, Rodgers H. Randomised controlled trial of a comprehensive stroke education programme for patients and carers. Proceedings of The Challenge of Stroke. The Lancet Conference. Montreal, Canada. October 1998.
-
- Rodgers H, Atkinson C, Bond S, Suddes M, Dobson R, Curless R. Randomised controlled trial of a comprehensive stroke education program for patients and caregivers. Stroke 1999;30:2585‐91. - PubMed
-
- Rodgers H, Curless R, Bond S, Suddes M. A randomised trial of a comprehensive stroke information service for patients and carers. Report to Northern and Yorkshire NHS Executive Unpublished. [Project Number: HSR/067]
Smith 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Smith J, Forster A, Young J. A randomized trial to evaluate an education programme for patients and carers after stroke. Clinical Rehabilitation 2004;18(7):726‐36. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Adie 2010 {published data only}
-
- Adie K, James M. Does telephone follow‐up improve blood pressure after minor stroke or TIA?. Age Ageing 2010;39(5):598‐603. - PubMed
Allen 2009 {published data only}
Andersen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Andersen HE, Eriksen K, Brown A, Schultz‐Larsen K, Forchhammer BE. Follow‐up services for stroke survivors after hospital discharge ‐ a randomized control study. Clinical Rehabilitation 2002;16(6):593‐603. - PubMed
Ayana 2000 {published data only}
-
- Ayana M, Pound P, Ebrahim S. Development and use of a patient held record to improve the coordination of services between the hospital and the community after stroke. NHS Executive, London Regional Office, Commissioned R & D programme, 2000. [National Research Register N0256033066]
Bacchini 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bacchini M, Rovacchi C, Chiampo F, Rossi, M. Gait analysis outcome following re‐education in patients poststroke. Gait and Posture 2011;33:S53‐S54.
Bakas 2008 {published data only}
Battersby 2009 {published data only}
-
- Battersby M, Hoffmann S, Cadilhac D, Osborne R, Lalor E, Lindley R. Getting your life back on track after stroke: a phase II multi‐centered, single‐blind, randomized, controlled trial of the Stroke Self‐Management Program vs. the Stanford Chronic Condition Self‐Management Program or standard care in stroke survivors. International Journal of Stroke 2009;4(2):137‐44. - PubMed
-
- Cadilhac DA, Hoffmann S, Kilkenny M, Lindley R, Lalor E, Osborne RH, et al. A phase II multicentered, single‐blind, randomized, controlled trial of the stroke self‐management program. Stroke 2011;42(6):1673‐9. - PubMed
Boter 2004 {published data only}
-
- Boter H. Multicenter randomized controlled trial of an outreach nursing support program for recently discharge stroke patients. Stroke 2004;35(12):2867‐72. - PubMed
Boysen 2007 {published data only}
Brier 2011 {published data only}
-
- Brier J, Carpentier M, Moreau J. Helping patients learn new skills: does involving CVA patients and their families in the design of a patient education program improve outcomes?. Clinical Nurse Specialist 2011;25(2):85‐6.
Brotons 2007 {published data only}
-
- Brotons C, Soriano N, Moral I, Rodrigo MP, Kloppe P, Rodriguez AI, et al. Randomized clinical trial to assess the efficacy of a comprehensive programme of secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease in general practice: the PREseAP study. Revista Espanola de Cardiologia 2011;64(1):13‐20. - PubMed
Burton 2005 {published data only}
-
- Burton C, Gibbon B. Expanding the role of the stroke nurse: a pragmatic clinical trial. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2005;52:640‐50. - PubMed
Byers 2010 {published data only}
-
- Byers A, Lamanna L, Rosenberg A. Enhanced stroke education using motivational interviewing increases patient knowledge and satisfaction after discharge from an acute care setting. Canadian Journal of Neuroscience Nursing 2010;32(1):22.
Chaiyawat 2009 {published data only}
Chang 2000 {published data only}
-
- ChangT, Li I. The effect of social support intervention on home‐bound stroke patients' physical and mental health in the Ilan area. Journal of Nursing Research (China) 2000;8(4):423‐34.
Chang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chang K, Zhang H, Xia Y, Chen C. Testing the effectiveness of knowledge and behavior therapy in patients of hemiplegic stroke. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation 2011;18(5):525‐35. - PubMed
Cheng 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cheng EM, Cunningham WE, Towfighi A, Sanossian N, Bryg RJ, Anderson TL. Randomized, controlled trial of an intervention to enable stroke survivors throughout the Los Angeles County safety net to "stay with the guidelines". Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes 2011;4:229‐34. - PMC - PubMed
Christie 1984 {published data only}
-
- Christie D, Weigall D. Social work effectiveness in two‐year stroke survivors: a randomised controlled trial. Community Health Studies 1984;8:26‐32. - PubMed
Chumbler 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chumbler NR, Roudebush RL, Morey MC, Griffiths P, Quigley P, Rose DK, et al. The effects of a stroke telerehabilitation in‐home intervention on function and disability: preliminary results of a randomized clinical trial. Stroke 2011;42(3):e76‐7.
Claiborne 2006 {published data only}
-
- Claiborne N. Effectiveness of a care coordination model for stroke survivors: a randomized study. Health and Social Work 2006;31(2):87‐96. - PubMed
Clark 2003 {published data only}
-
- Clark MS, Rubenach S, Winsor A. A randomized controlled trial of an education and counselling intervention for families after stroke. Clinical Rehabilitation 2003;17(7):703‐12. - PubMed
Clarke 2011 {published data only}
-
- Clarke A, Barker‐Collo SL, Feigin VL. Educational group treatment for post‐stroke fatigue: a randomised pilot trial. Brain Impairment 2011;12:63.
-
- Clarke A, Barker‐Collo SL, Feigin VL. Poststroke fatigue: does group education make a difference? A randomized pilot trial. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation 2012;19(1):32‐9. - PubMed
Dennis 1997 {published data only}
-
- O'Rourke SJ, Dennis MS, Slattery J, Warlow CP. Preliminary results from a randomised trial of a stroke family care worker; patients outcome six months post stroke. Age and Ageing 1996;25 Suppl 1:32.
Desrosiers 2007 {published data only}
-
- Desrosiers J, Noreau L, Rochette A, Carbonneau H, Fontaine L, Viscogliosi C, et al. A home leisure education program may reduce depression after a stroke. Stroke 2007;38(2):473‐4. - PubMed
-
- Desrosiers J, Noreau L, Rochette A, Viscogliosi C, Bravo G. Effect of a home leisure education program after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2007;88(9):1095‐100. - PubMed
Dongbo 2003 {published data only}
Ertel 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ertel K, Glymour M, Glass T, Berkman L. Frailty modifies effectiveness of psychosocial intervention in recovery from stroke. Clinical Rehabilitation 2007;21(6):511‐2. - PubMed
Evans 1984 {published data only}
-
- Evans RL, Held S. Evaluation of family stroke education. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 1984;7(1):47‐51. - PubMed
Folden 1993 {published data only}
-
- Folden SL. The effect of supportive‐educative nursing interventions in poststroke older adults' self‐care perceptions. Miami, Florida: University of Miami, 1990.
-
- Folden SL. Effect of a supportive‐educative nursing intervention on older adults' perceptions of self‐care after a stroke. Rehabilitation Nursing 1993;18:162‐7. - PubMed
Forster 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dowswell G, Lawler J, Young J, Forster A, Hearn J. A qualitative study of specialist nurse support for stroke patients and care‐givers at home. Clinical Rehabilitation 1997;11:283‐301. - PubMed
Friedland 1992 {published data only}
-
- Friedland J, McColl M. Social support for stroke survivors: development and evaluation of an intervention programme. Physical and Occupational Therapy in Geriatrics 1989;7(3):55‐69.
-
- Friedland JF, McColl M. Social support intervention after stroke: results of a randomised trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1992;73:573‐81. - PubMed
Gillham 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gillham S, Endacott R. Impact of enhanced secondary prevention on health behaviour in patients following minor stroke and transient ischaemic attack: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2010;24(9):822‐30. - PubMed
Glass 2004 {published data only}
-
- Glass T, Berkman L, Hiltunen E, Furie K, Glymour M, Fay M, et al. The Families In Recovery from Stroke Trial (FIRST): primary study results. Psychosomatic Medicine 2004;66(6):889‐97. - PubMed
Goldberg 1997 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg G, Segal ME, Berk SN, Schall RR, Gershkoff AM. Stroke transition after inpatient rehabilitation. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation 1997;4:64‐79. - PubMed
Grant 2002 {published data only}
-
- Grant JS, Elliott TR, Weaver M, Bartolucci AA, Giger JN. Telephone intervention with family caregivers of stroke survivors after rehabilitation. Stroke 2002;38(8):2060‐5. - PubMed
Grasel 2006 {published data only}
-
- Grasel E, Schmidt R, Biehler J, Schupp W. Long‐term effects of the intensification of the transition between inpatient neurological rehabilitation and home care of stroke patients. Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;20(7):577‐83. - PubMed
Green 2006 {published data only}
-
- Green T, Haley E, Eliasziw M, Hoyte K. Education in stroke prevention: efficacy of an educational counselling intervention to increase knowledge in stroke survivors. Canadian Journal of Neuroscience Nursing 2007;29(2):13‐20. - PubMed
Habibzadeh 2007 {published data only}
-
- Habibzadeh H, Gofranipoor F, Ahmadi F. A study on the effect of self care plan on activity daily living status in patient with cerebrovascular accident. Journal of Medical Sciences 2007;7(1):126‐30.
Harari 2004 {published data only}
-
- Harari D, Norton C, Lockwood L, Swift C. Treatment of constipation and fecal incontinence in stroke patients: randomised controlled trial. Stroke 2004;35:2549‐55. - PubMed
Harrington 2010 {published data only}
-
- Harrington R, Taylor G, Hollinghurst S, Reed M, Kay H, Wood, V. A community‐based exercise and education scheme for stroke survivors: a randomized controlled trial and economic evaluation. Clinical Rehabilitation 2010;24(1):3‐15. - PubMed
Hartke 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hartke R, King R. Head trauma and stroke. The effectiveness of a telephone support group for stroke caregivers. Rehabilitation R&D Progress Reports May 1997:124‐5.
-
- Hartke RJ, King RB. Telephone group intervention for older stroke caregivers. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation 2003;9(4):65‐81. - PubMed
Harwood 2006 {published data only}
-
- Harwood M. A randomised controlled study to measure the effectiveness of an educational video compared to a goal setting exercise and to a control (written pamphlet) in the treatment of stroke to improve stroke recovery for Maori and Pacific people and their families. http://www.anzctr.org.au/trial (accessed August 2011).
-
- Harwood M, Weatherall M, Talemaitoga A, Barber PA, Gommans J, Taylor W, et al. Taking charge after stroke: promoting self‐directed rehabilitation to improve quality of life – a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2012;26(6):493‐501. - PubMed
Hochstenbach 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hochstenbach J, Mulder T. The development and evaluation of a treatment program directed at the improvement of psychosocial behaviour following stroke. Veterans Administration Database of Research in Progress, 1999.
Holzemer 2011 {published data only}
-
- Holzemer E, Thanavaro J, Malmstrom T, Cruz‐Flores S. Modifying risk factors after TIA and stroke: the impact of intensive education. Journal for Nurse Practitioners 2011;7(5):372‐7.
Huijbregts 2009 {published data only}
Jones 2009 {published data only}
-
- Jones F, Mandy A, Partridge C. Changing self‐efficacy in individuals following a first time stroke: preliminary study of a novel self‐management intervention. Clinical Rehabilitation 2009;23(6):522‐33. - PubMed
Kendall 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kendall E, Catalano T, Kuipers P, Posner N, Buys N, Charker J. Recovery following stroke: the role of self‐management education. Social Science and Medicine 2007;64(3):735‐46. - PubMed
Leathley 2003 {published data only}
-
- Leathley M, Fall S, Sharma A, Watkins C, Barer D. Life after stroke: multicentre trial of psychosocial interventions after stroke. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2003;16 Suppl 4:70.
Lincoln 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lincoln NB, Francis VM, Lilley SA, Sharma JC, Summerfield M. Evaluation of a stroke family support organiser: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2003;34(1):116‐21. - PubMed
Linn 1979 {published data only}
-
- Linn JT. Medications for the elderly. Medical Journal of Australia 1979;1:315‐6. - PubMed
Lorenc 1992 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lorenc L, Sturmey P, Brittain H. Evaluation of a meta‐cognitive strategy to improve the information gained from a stroke information pack. Stress Medicine 1992;8(2):111‐2.
Mackay‐Lyons 2010 {published data only}
-
- MacKay‐Lyons M, Gubitz G, Giacomantonio N, Wightman H, Marsters D, Thompson K, et al. Program of rehabilitative exercise and education to avert vascular events after non‐disabling stroke or transient ischemic attack (PREVENT Trial): a multi‐centred, randomised controlled trial. BMC Neurology 2010;10:122. - PMC - PubMed
Mant 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mant J, Carter J, Wade DT, Winner S. Family support for stroke: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2000;356:808‐13. - PubMed
McKinney 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- McKinney M, Blake H, Treece KA, Lincoln N, Playford D, Gladman JRF. Evaluation of a cognitive assessment in stroke rehabilitation. Clinical Rehabilitation 2002;16:129‐36. - PubMed
-
- McKinney M, Playford D, Lincoln N, Blake H, Treece K. Evaluation of cognitive assessment after stroke. Stroke Association Conference Proceedings. 2000.
Morrison 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Morrison VL, Johnston M, MacWalter RS, Pollard BS. Improving emotional outcomes following acute stroke: a preliminary evaluation of a work‐book based intervention. Scottish Medical Journal 1998;43(2):52‐3. - PubMed
Napolitan 1999 {published data only}
-
- Napolitan SM. An evaluation of the effectiveness of early psychoeducational orientation and home visit intervention for first‐time caregivers of stroke patients. Dissertation Abstracts. Dissertation Abstracts, 1999. [ISBN 0‐599‐32429‐8]
Neubert 2011 {published data only}
-
- Neubert S, Sabariego C, Stier‐Jarmer M, Cieza A. Development of an ICF‐based patient education program. Patient Education & Counseling 2011;84(2):e13‐7. - PubMed
Nguyen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Nguyen V‐HV, Poon J, Tokuda L, Sayers J, Wallis R‐A, Dergalust S. Pharmacist telephone interventions improve adherence to stroke preventive medications and reduce stroke risk factors: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2011;42(3):e244.
Nir 2006 {published data only}
-
- Nir Z, Weisel‐Eichler A. Improving knowledge and skills for use of medication by patients after stroke: evaluation of a nursing intervention. American Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2006;85(7):582‐92. - PubMed
Nour 2002 {published data only}
-
- Nour K, Desrosiers J, Gauthier P, Carbonneau H. Impact of a home leisure educational program for older adults who have had a stroke. Therapeutic Recreation Journal 2002;36(1):48‐64.
Oupra 2010 {published data only}
-
- Oupra R, Griffiths R, Pryor J, Mott S. Effectiveness of Supportive Educative Learning programme on the level of strain experienced by caregivers of stroke patients in Thailand. Health and Social Care in the Community 2010;18(1):10‐20. - PubMed
Pierce 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pierce L, Steiner V, Khuder S, Govoni A, Horn L. The effect of a Web‐based stroke intervention on carers' well‐being and survivors' use of healthcare services. Disability and Rehabilitation 2009;31(20):1676‐84. - PubMed
-
- Steiner V, Pierce L, Windnagel F, Martincin K, Pawlak R, Salvador D. The impact of a web‐based caregiver intervention on the reasons stroke survivors use health care services during the first year post treatment. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation 2009;16(2):122‐32. - PubMed
Printz‐Feddersen 1990 {published data only}
-
- Printz‐Feddersen V. Group process on caregiver burden. Journal of Neuroscience Nursing 1990;22(3):164‐8. - PubMed
Redfern 2008 {published data only}
-
- Redfern J, McKevitt C, Rudd A, Heuschmann P, Grieve A, Wolfe C. Stop stroke: cluster randomised controlled trial of a patient/carer and general practitioner intervention to improve risk factor management after stroke. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2009;27:66.
-
- Redfern J, Rudd A, Wolfe C, McKevitt C. Stop stroke: development of an innovative intervention to improve risk factor management after stroke. Patient Education and Counseling 2008;72(2):201‐9. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe C, Redfern J, Rudd A, Grieve A, Heuschmann P, McKevitt C. Cluster randomized controlled trial of a patient and general practitioner intervention to improve the management of multiple risk factors after stroke: stop stroke. Stroke 2010;41(11):2470‐6. - PubMed
Rimmer 2000 {published data only}
-
- Rimmer JH, Braunschweig C, Silverman K, Riley B, Creviston T, Nicola T. Effects of a short‐term health promotion intervention for a predominantly African‐American group of stroke survivors. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2000;18(4):332‐8. - PubMed
Sahebalzamani 2009 {published data only}
-
- Sahebalzamani M, Aliloo L, Shakibi A. The efficacy of self‐care education on rehabilitation of stroke patients. Saudi Medical Journal 2009;30(4):550‐4. - PubMed
Sanguinetti 1987 {published data only}
-
- Sanguentetti M, Cantanzaro M. A comparison of discharge teaching on the consequences of brain injury. Journal of Neuroscience Nursing 1987;19:271‐5. - PubMed
Shyu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Shyu Y, Chen M, Chen S, Wang H, Shao J. A family caregiver‐oriented discharge planning program for older stroke patients and their family caregivers. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2008;17(18):2497‐508. - PubMed
-
- Shyu Y, Kuo L, Chen M, Chen S. A clinical trial of an individualised intervention programme for family caregivers of older stroke victims in Taiwan. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2010;19(11‐12):1675‐85. - PubMed
Sit 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sit J, Yip V, Stanley K, Gun A, Lee J. A quasi‐experimental study on a community‐based stroke prevention programme for clients with minor stroke. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2007;16(2):272‐81. - PubMed
Skidmore 2008 {published data only}
Tilling 2005 {published data only}
-
- Tilling K, Coshall C, McKevitt C, Daneski K, Wolfe C. A family support organiser for stroke patients and their carers: a randomised controlled trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2004;20(2):85‐91. - PubMed
Towle 1989 {published data only}
-
- Towle D, Lincoln NB, Mayfield LM. Evaluation of social work on depression after stroke. Clinical Rehabilitation 1989;3:89‐96.
van den Heuvel 2000 {published data only}
-
- Schure L, Heuvel E, Stewart R, Sanderman R, Witte L, Meyboom‐de Jong B. Beyond stroke: description and evaluation of an effective intervention to support family caregivers of stroke patients. Patient Education and Counseling 2006;62(1):46‐55. - PubMed
-
- Heuvel ETP, Witte LP, Nooyen‐Haazen I, Sanderman R, Meyboom‐de Jong B. Short‐term effects of a group support program and an individual support program for caregivers of stroke patients. Patient Education and Counseling 2000;40:109‐20. - PubMed
-
- Heuvel ETP, Witte LP, Stewart RE, Schure LM, Sanderman R, Meyboom‐de Jong B. Long‐term effects of a group support program and an individual support program for informal caregivers of stroke patients: which caregivers benefit the most?. Patient Education and Counselling 2002;47:291‐9. - PubMed
Winkens 2009 {published data only}
-
- Winkens I, Heugten C, Wade D, Habets E, Fasotti L. Efficacy of time pressure management in stroke patients with slowed information processing: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2009;90(10):1672‐9. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Aben 2012 {published data only}
-
- Aben L, Heijenbrok‐Kal M, Ponds R, Busschbach J, Ribbers G. Long term effects of a memory self‐efficacy training program for stroke patients in the chronic stage: a randomized controlled trial. Brain Injury 2012;26(4‐5):414‐5.
Andrea 2003 {published data only}
-
- Andrea S, Kotzabassaki S, Bellou M, Vardaki Z. Evaluation of the effectiveness of a self‐care educational program on activities of daily living, performed by hemiplegic patients. ICUs and Nursing Web Journal 2003; Vol. Oct‐Dec, issue 16.
Bodin 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bodin S, Labrunee‐Prod'homme K, Delort‐Albrespit I, Castel‐Lacanal E, Labrunee M, Marque P, et al. Impact of early information of close relative about communication with an aphasic patient: InfoCom study. Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine 2011;54:e215.
Bonita 1995 {unpublished data only}
-
- Bonita R. Provision of an information leaflet. Unpublished.
Cameron 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cameron JI, Naglie G, Green T, Gignac MAM, Bayley M, Huijbregts M, et al. The Timing It Right Stroke Family Support Program: phase 2 pilot randomized controlled trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2011;31 Suppl 2:42.
Choi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Choi JS, Seo YM, Kwon IS. Effects of education on knowledge and practice of caregivers of the stroke patient. Taehan Kanho Hakhoe Chi 2006;36(7):1175‐82. - PubMed
Eames 2008 {published data only}
-
- Eames S. Evaluation of a post‐discharge education and support package for stroke clients and their carers: randomised control trial (Does providing information after stroke help?). http://www.anzctr.org.au/trial (accessed November 2011).
-
- Eames S, Hoffmann T, Worrall L, Wong A, Read S. Evaluation of an innovative post‐discharge education and support package for patients with stroke and their carers. International Journal of Stroke 2010;5 Suppl 2:190.
-
- Emmes S, Hoffman T, Worrall L, Read S, Wong A. Randomised controlled trial of a postdischarge education and support package for clients with stroke and their carers. Australian Occupational Therapy Journal 2011;58:51.
Heier 2002 {published data only}
-
- Heier H, Laemmler G, Steinhagen‐Thiessen E. Evaluation of a psychoeducative intervention program for caregivers of stroke patients. Zeitschrift Fuer Neuropsychiogie 2002;13(3):201‐9.
Jian 1998 {published data only}
-
- Jian S, Chi LI. A study of patient education for stroke survivors in Wuhan, China. Annals of Oncology 1998;9(53):119.
Kim 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kim CG, Park HA. Development and evaluation of a web‐based education program to prevent secondary stroke. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2011;41(1):47‐60. - PubMed
Ostwald 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ostwald S. Intervention for stroke survivors and their spousal caregivers. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 1 November 2011).
Piano 2010 {published data only}
-
- Piano AN, Roxas AA, Aganon F, Ticod MLJC, Sibulo JV, Cajucom T, et al. Stroke awareness among stroke victors: a randomized open label clinical trial comparing videobased stroke education program vs. nurse education. International Journal of Stroke 2010;5 Suppl 2:281.
Sun 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sun M, Ling XM, Yu DF. Effects of personalized health education on quality of life in patients with stroke. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University (Medical Science) 2011;31(7):996‐9.
Tuncay 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tuncay FO, Mollaoglu M. The effect of a self‐care education program on cerebrovascular disease patients' activities of daily living. Neurology Psychiatry and Brain Research 2006;13(2):83‐8.
References to ongoing studies
Boden‐Albala 2007 {published data only}
-
- Boden‐Albala B, Sacco R, Stillman JI, Wright CB. The Stroke Warning Information and Faster Treatment Study (SWIFT). http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00415389?term=SWIFT&rank=7(acc... December 2011).
-
- Boden‐Albala B, Stillman J, Chong J, Perez T, Rivolta J, Evenson L, et al. Transient cerebral ischemia is associated with earlier ED arrival times than ischemic stroke: the Stroke Warning Information and Faster Treatment (SWIFT) study. Stroke 2007;38(2):502.
-
- Stillman J, Chong J, Perez T, Cheung P, Paik MC, Sacco RL, et al. Are stroke patients knowledgeable and prepared for a recurrent event? Findings from the SWIFT study. Stroke 2007;38(2):527.
Damush 2006 {published data only}
-
- Damush TM. Adapting tools to implement stroke risk management to veterans (TOOLS). http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00355147?term=TOOLS&rank=1 (accessed November 2011).
Dromerick 2008 {published data only}
-
- Dromerick AW. Preventing Recurrence Of Thromboembolic Events through Coordinated Treatment in the District of Columbia (PROTECT DC). http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00703274?term=PROTECT+DC&rank=1 (accessed November 2011). - PMC - PubMed
Graven 2008 {published data only}
Hackett 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hackett ML, Carter G, Crimmins D, Clarke T, Maddock K, Sturm JW. imProving Outcomes after STroke clinical pilot trial protocol (POST). International Journal of Stroke 2010;5(10):52‐6. - PubMed
Hoffmann 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hoffmann T. Do stroke patients receiving either a self‐management or cognitive‐behavioural intervention demonstrate enhanced early emotional adjustment as compared with those receiving usual care?. http://www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?ID=308355 (accessed Novemeber 2011).
O'Carroll 2010 {published data only}
Rochette 2008 {published data only}
Shaughnessy 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shaughnessy M. Reshaping Exercise Habits and Beliefs (REHAB). http://www.clinicaltrial.gov/ (accessed November 2011).
Young 2007 {published data only}
-
- Young C. Education to increase self efficacy for patients having rehabilitation after monophasic neurological disability. www.nrr.nhs.uk/ (accessed March 2007).
Additional references
Adams 1998
-
- Adams RD, Victor M, Ropper, AH. Principles of Neurology: Companion Handbook. 6th Edition. McGraw‐Hill, 1998.
Adamson 2004
-
- Adamson J, Beswick A, Ibrahim S. Is stroke the most common cause of disability?. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2004;13(4):171‐7. - PubMed
Aho 1980
Brown 1990
-
- Brown SA. Studies of educational interventions and outcomes in diabetic adults: a meta‐analysis revisited. Patient Education and Counseling 1990;16:189‐215. - PubMed
Canadian Stroke Network 2006
-
- Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care, Ottawa 2006. Canadian Stroke Network and the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada: Canadian Stroke Strategy.
Care Quality Commission 2011
-
- Care Quality Commission. Supporting life after stroke. Care Quality Commission, London 2011.
Coulter 1998
-
- Coulter A, Entwhistle V, Gilbert D. Informing patients: an assessment of the quality of patient information materials. Kings Fund, London 1998.
de Beurs 1999
-
- Beurs E, Bouter LM. Is the standardised mean difference a suitable measure of treatment effect?. Proceedings of the 7th Cochrane Colloquium, Universita S. Tommaso D'Aquino, Rome. 1999.
Deeks 2001
-
- Deeks JJ, Altman DG, Bradburn MJ. Statistical methods for combining results from several studies in meta‐analysis. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Health Care: Meta‐Analysis in Context. 2nd Edition. London: BMJ Publication Group, 2001.
Department of Health 2001
-
- The expert patient: a new approach to chronic disease management for the 21st century. Department of Health, London 2001.
Department of Health 2007
-
- Department of Health. National STROKE Strategy. Department of Health, London 2007.
Department of Health 2010
-
- Equity and Excellence: Liberating the NHS. Department of Health, London 2010.
Drummond 1996
-
- Drummond A, Lincoln N, Juby L. Effects of a stroke unit on knowledge of stroke and experiences in hospital. Health Trends 1996;28:26‐30.
Duncan 1999
-
- Duncan P, Wallace D, Lai S, Johnson D, Embretson S, Laster L. The stroke impact scale version 2.0. Evaluation of reliability, validity, and sensitivity to change. Stroke 1999;30(10):2131‐40. - PubMed
Eames 2011
-
- Eames S, Hoffmann T, Worrall L, Read S. Delivery styles and formats for different stroke information topics: patient and carer preferences. Patient Education and Counseling 2011;84:e18‐e23. - PubMed
Ellis 2010
EuroQol Group 1990
-
- The Euroqol Group. EuroQol: a new facility for the measurement of health related quality of life. Health Policy 1990;16:199‐208. - PubMed
Evans 1985
-
- Evans RL, Pomeroy S, Weele T, Hammond MC. Reliability of a stroke care information test for family caretakers. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 1985;8:199‐201.
Evans 1991
-
- Evans RL, Bishop DS, Haselkorn JK. Factors predicting satisfactory home care after stroke. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1991;72:144‐7. - PubMed
Farran 1995
-
- Farran CJ, Herth KA, Popovich JM. Hope and hopelessness: critical clinical constructs. Sage Publications, 1995.
Firth 1991
-
- Frith B. Giving information to radiotherapy patients. Nursing Standard 1991;5(34):33‐5. - PubMed
Gallagher 1982
-
- Gallagher D, Nies G, Thompson LW. Reliability of the Beck Depression Inventory with older adults. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2000;50:152‐3. - PubMed
Gibbs 1989
Goldberg 1979
-
- Goldberg DP, Hillier VF. A scaled version of the General Health Questionnaire. Psychological Medicine 1979;9:139‐45. - PubMed
Goldberg 1988
-
- Goldberg D, Williams P. A User's Guide to the General Health Questionnaire. Windsor, UK: NFER‐Nelson Publishing Company Limited, 1988.
Grimshaw 2001
-
- Grimshaw J, Shirran L, Thomas R, Mowatt G, Fraser C, Bero L, et al. Changing provider behaviour. An overview of systematic reviews of interventions. Medical Care 2001;39(8 Suppl 2):II‐2‐II‐45. - PubMed
Hafsteinsdottir 2011
-
- Hafsteinsdottir TB, Vergunst M, Lindeman E, Schuurmans M. Educational needs of patients with a stroke and their caregivers: a systematic review of the literature. Patient Education and Counseling 2011;85(1):14‐25. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Holbrook 1983
-
- Holbrook M, Skilbeck CE. An activities index for use with stroke patients. Age and Ageing 1983;12:166‐70. - PubMed
Knapp 2000
-
- Knapp P, Young J, House A, Forster A. Non‐drug strategies to resolve psycho‐social difficulties after stroke. Age and Ageing 2000;29(1):23‐30. - PubMed
Lewin 1992
-
- Lewin B. A self‐help post‐MI rehabilitation package ‐The Heart Manual: effects on psychological adjustment, hospitalisation and GP consultation. Lancet 1992;339:1036‐40. - PubMed
Li 2011
Mackenzie 2007
-
- Mackenzie A, Perry L, Lockhart E, Cottee M, Cloud G, Mann H. Family carers of stroke survivors: needs, knowledge, satisfaction and competence in caring. Disability and Rehabilitation 2007;29(2):111‐21. - PubMed
Mahoney 1994
-
- Mahoney J, Drinka TJK, Abler R. Screening for depression: single question versus GDS. Journal of American Geriatric Society 1994;9:1006‐8. - PubMed
McKevitt 2011
-
- McKevitt C, Fudge N, Redfern J, Sheldenkar A, Crichton S, Rudd AR, et al. Self‐reported long‐term needs after stroke. Stroke 2011;42(5):1398‐403. - PubMed
Morrison 2000
-
- Morrison V, Johnston M, Walter RM. Predictors of distress following an acute stroke: disability, control cognitions, and satisfaction with care. Psychology and Health 2000;15(3):395‐408.
Mukherjee 2011
-
- Mukherjee D, Patil CG. Epidemiology and the global burden of stroke. World Neurosurgery 2011;76(6 Suppl):S85‐90. - PubMed
National Audit Office 2005
-
- National Audit Office. Reducing brain damage: faster access to better stroke care. London, NAO 2005.
National Stroke Foundation Australia 2010
-
- Clinical Guidelines for Stroke Management, Melbourne 2010. National Stroke Foundation Australia.
Nouri 1987
-
- Nouri FM, Lincoln NB. An extended activities of daily living for stroke patients. Clinical Rehabilitation 1987;1:301‐5.
O'Mahoney 1997
-
- O'Mahoney PG, Rodgers H, Thomson RG, Dobson R, James OFW. Satisfaction with information and advice received by stroke patients. Clinical Rehabilitation 1997;11:68‐72. - PubMed
OAST 2007
-
- The Optimising Analysis of Stroke Trials (OAST) Collaboration. Can we improve the statistical analysis of stroke trials? Statistical re‐analysis of functional outcomes in stroke trials. Stroke 2007;38:1911‐5. - PubMed
Partridge 1989
-
- Partridge C, Johnston M. Perceived control of recovery from physical disability: measurement and prediction. British Journal of Clinical Psychology 1989;28(Pt 1):53‐9. - PubMed
Patrick 1989
-
- Patrick DL, Peach H (Eds). Disablement in the community. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1989.
Pound 1993
Pound 1994
-
- Pound P, Gompertz P, Ebrahim S. Patients' satisfaction with stroke services. Clinical Rehabilitation 1994;8:7‐17.
RCP 2008
-
- Royal College of Physicians. National clinical guideline for stroke, 3rd edition. Royal College of Physicians, London 2008.
Riemsma 2003
Rowan 1994
-
- Rowan K. Global questions and scores. In: Jenkinson C editor(s). Measuring Health and Medical Outcomes. London: UCL Press, 1994.
Sakthong 2007
-
- Sakthong P, Schommer J, Gross C, Sakulbumrungsil R, Prasithsirikul W. Psychometric properties of WHOQOL‐BREF‐Thai in patients with HIV/AIDS. Journal of Medical Association of Thailand 2007;90:2449‐57. - PubMed
Sheikh 1986
-
- Sheikh JI, Yesavage JA. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS): recent evidence and development of a shorter version. Clinical Gerontology: A Guide to Assessment and Intervention. New York: The Haworth Press, 1986:165‐73.
Sullivan 2004
-
- Sullivan K, Dunton N. Development and validation of the Stroke Knowledge Test. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation 2004;11:19‐28. - PubMed
Theis 1995
-
- Theis AL, Johnson JH. Strategies for teaching patients: a meta‐analysis. Clinical Nurse Specialist 1995;9:100‐5. - PubMed
Ware 1992
-
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36‐item short‐form health survey (SF‐36). Medical Care 1992;30:473‐83. - PubMed
Wellwood 1994
-
- Wellwood I, Dennis MS, Warlow CP. Perceptions and knowledge of stroke amongst surviving patients with stroke and their carers. Age and Ageing 1994;23:293‐8. - PubMed
Zigmond 1983
-
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;67:361‐70. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Forster 2001
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

