Psychological therapies for pathological and problem gambling
- PMID: 23152266
- PMCID: PMC11955261
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008937.pub2
Psychological therapies for pathological and problem gambling
Abstract
Background: Various psychological therapies for pathological and problem gambling have been evaluated in randomised trials. A synthesis of best-quality evidence is required.
Objectives: The objective was to synthesise evidence from randomised trials of psychological therapies for pathological and problem gambling (cognitive-behaviour therapy (CBT), motivational interviewing therapy, integrative therapy, other psychological therapy), in order to indicate the efficacy of therapies and durability of therapy effects, relative to control conditions.
Search methods: We conducted a search of the Cochrane Depression, Anxiety and Neurosis Review Group's Specialised Register (CCDANCTR), which includes relevant randomised controlled trials from the following bibliographic databases: CENTRAL (The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials) (all years), EMBASE (1974 -), MEDLINE (1950 -) and PsycINFO (1967 -). We also carried out complementary searches of MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, LILACS and CENTRAL for studies published between January 1980 and October 2011. We examined the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform and ClinicalTrials.gov and also conducted manual searches of selected journals and reference lists of included studies.
Selection criteria: Included studies were clinical trials using random allocation to groups, considering pathological or problem gamblers, and evaluating a psychological therapy for pathological or problem gambling. Control conditions included 'no treatment' controls, referral to Gamblers Anonymous and non-specific treatment component controls.
Data collection and analysis: We systematically extracted data on the characteristics and results of studies. Primary outcomes were measures of gambling symptom severity, financial loss from gambling and frequency of gambling. Secondary outcomes were occurrence of pathological gambling diagnoses and depression and anxiety symptoms. Treatment effects were defined by comparisons between therapy and control conditions at post-treatment assessments (conducted from 0 to 3 months following completion of treatment) and follow-up assessments (conducted from 9 to 12 months following completion of treatment), respectively, using the standardised mean difference (SMD) or risk ratio (RR). We synthesised results through random-effects meta-analysis.
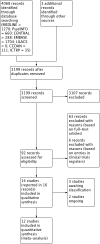
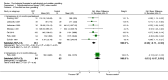
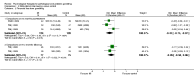
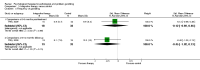
Main results: Fourteen studies (n = 1245) met the inclusion criteria. Eleven studies compared CBT with control and comparisons at 0 to 3 months post-treatment showed beneficial effects of therapy that ranged from medium (when defined by financial loss from gambling: SMD -0.52; 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.71 to -0.33, n = 505) to very large (for gambling symptom severity: SMD -1.82; 95% CI -2.61 to -1.02, n = 402). Only one study (n = 147) compared groups at 9 to 12 months follow-up and produced smaller effects that were not significant. Four studies of motivational interviewing therapy were identified and mainly considered samples demonstrating less severe gambling (relative to studies of pathological gamblers). Data suggested reduced financial loss from gambling following motivational interviewing therapy at 0 to 3 months post-treatment (SMD -0.41; 95% CI -0.75 to -0.07, n = 244), although comparisons on other outcomes were not significant. The effect approached zero when defined by gambling symptom severity (SMD -0.03; 95% CI -0.55 to 0.50, n = 163). Studies compared groups at 9 to 12 months follow-up and found a significant effect of motivational interviewing therapy in terms of frequency of gambling (SMD -0.53; 95% CI -1.04 to -0.02, n = 62), with comparisons on other outcomes that were not significant. Two studies of integrative therapies also considered samples demonstrating overall low gambling severity, and found no significant effects of therapy at 0 to 3 months post-treatment. Comparisons at 9 to 12 months follow-up suggested a medium effect from therapy in terms of gambling symptom severity, with no significant differences for other outcomes. One study (n = 18) considered another psychological therapy (i.e.Twelve-Step Facilitated Group Therapy) and suggested beneficial effects in terms of most outcomes at 0 to 3 months post-treatment. The evidence supporting these various classes of therapy ranged from very low to low quality.
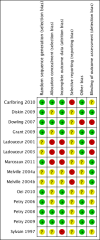
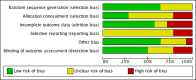
Authors' conclusions: This review supports the efficacy of CBT in reducing gambling behaviour and other symptoms of pathological and problem gambling immediately following therapy. However, the durability of therapeutic gain is unknown. There is preliminary evidence for some benefits from motivational interviewing therapy in terms of reduced gambling behaviour, although not necessarily other symptoms of pathological and problem gambling. However, the findings are based on few studies and additional research is needed to inform conclusions. There is also evidence suggestive of some possible benefit from integrative therapies, and other psychological therapies for pathological and problem gambling. However, there are too few studies and evidence is insufficient to evaluate these therapies. The majority of studies in this review varied in risk of bias, and much of the evidence comes from studies with multiple limitations. The current data may thus reflect overestimates of treatment efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures















Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008937
References
References to studies included in this review
Carlbring 2010 {published data only}
Diskin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Diskin KM, Hodgins DC. A randomized controlled trial of a single session motivational intervention for concerned gamblers. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2009;47:382‐8. - PubMed
Dowling 2007 {published data only}
-
- Dowling N, Smith D, Thomas T. A comparison of individual and group cognitive‐behavioural treatment for female pathological gambling. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2007;45:2192‐202. - PubMed
-
- Dowling N, Smith D, Thomas T. Treatment of female pathological gambling: the efficacy of a cognitive‐behavioural approach. Journal of Gambling Studies 2006;22:355‐72. - PubMed
Grant 2009 {published data only}
Ladouceur 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ladouceur R, Sylvain C, Boutin C, Lachance S, Doucet C, Leblond J, et al. Cognitive treatment of pathological gambling. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 2001;189:774‐80. - PubMed
Ladouceur 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ladouceur R, Sylvain C, Boutin C, Lachance S, Doucet C, Leblond J. Group therapy for pathological gamblers: a cognitive approach. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2003;41:587‐96. - PubMed
Marceaux 2011 {published data only}
-
- Marceaux JC, Melville CL. Twelve‐step facilitated versus mapping enhanced cognitive‐behavioral therapy for pathological gambling: a controlled study. Journal of Gambling Studies 2011;27:171‐90. - PubMed
Melville 2004a {published data only}
-
- Melville CL, Davis CS, Matzenbacher DL, Clayborne J. Node‐link‐mapping‐enhanced group treatment for pathological gambling. Addictive Behaviors 2004;29:73‐87. - PubMed
Melville 2004b {published data only}
-
- Melville Cl, Davis CS, Matzenbacher DL, Clayborne J. Node‐link‐mapping‐enhanced group treatment for pathological gambling. Addictive Behaviors 2004;29:73‐87. - PubMed
Oei 2010 {published data only}
-
- Oei TPS, Raylu N, Casey LM. Effectiveness of group and individual formats of a combined motivational interviewing and cognitive behavioral treatment program for problem gambling: a randomized controlled trial. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy 2010;38:233‐8. - PubMed
Petry 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ledgerwood DM, Weinstock J, Morasco BJ, Petry NM. Clinical features and treatment prognosis of pathological gamblers with and without recent gambling‐related illegal behavior. Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law 2007;35(3):294‐301. - PubMed
-
- Morasco BJ, Weinstock J, Ledgerwood DM, Petry NM. Psychological factors that promote and inhibit pathological gambling. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice 2007;14(2):208‐17.
-
- Petry NM, Ammerman Y, Bohl J, Doersch A, Gay H, Kadden R, et al. Cogntive‐behavioral therapy for pathological gamblers. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2006;74(3):555‐67. - PubMed
-
- Petry NM, Litt MD, Kadden R, Ledgerwood DM. Do coping skills mediate the relationship between cognitive‐behavioral therapy and reductions in gambling in pathological gamblers?. Addiction 2007;102(8):1280‐91. - PubMed
Petry 2008 {published data only}
Petry 2009 {published data only}
Sylvain 1997 {published data only}
-
- Ladouceur R, Sylvain C. [Tratamiento del juego patologico: un estudio controlado]. Annuario de Psicologia 1999;30(4):127‐35.
-
- Sylvain C, Ladouceur R, Boisvert JM. Cognitive and behavioral treatment of pathological gambling: a controlled study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1997;65(5):727‐32. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Blanco 2010 {published data only}
-
- Blanco C. Gambling addiction: treatment mediators and moderators. ClinicalTrials.gov 2010; Vol. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01135264.
Carlbring 2008 {published data only}
-
- Carlbring P, Smit F. Randomized trial of internet‐delivered self‐help with telephone support for pathological gamblers. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2008;76(6):1090‐4. - PubMed
Cunningham 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cunningham JA, Hodgins DC, Toneatto T, Rai A, Cordingley J. Pilot study of a personalized feedback intervention for problem gamblers. Behavior Therapy 2009;40(3):219‐24. - PubMed
Dickerson 1990 {published data only}
-
- Dickerson M, Hinchy J, England SL. Minimal treatments and problem gamblers: a preliminary investigation. Journal of Gambling Studies 1990;6(1):87‐102. - PubMed
Echeburua 1996 {published data only}
-
- Echeburua E, Baez C, Fernandez‐Montalvo J. Comparative effectiveness of three therapeutic modalities in the psychological treatment of pathological gambling: long term outcome. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy 1996;24(1):51‐72.
-
- Echeburua E, Baez C, Fernandez‐Montalvo J. Differential effectiveness of several therapeutic approaches in the psychological treatment of pathological gambling [Efectividad diferencial de diversas modalidades terapéuticas en el tratamiento psicológico del juego patológico: un estudio experimental]. Análisis y Modificación de Conducta 1994;20(73):617‐43.
Echeburua 2000 {published data only}
-
- Echeburua E, Fernandez‐Montalvo J, Baez C. Relapse prevention in the treatment of slot‐machine pathological gambling: long‐term outcome. Behavior Therapy 2000;31(2):351‐64.
Echeburua 2011 {published data only}
-
- Echeburua E, Gomez M, Freixa M. Cognitive‐behavioural treatment of pathological gambling in individuals with chronic schizophrenia: a pilot study. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2011;49:808‐14. - PubMed
Harvey 2010 {published data only}
-
- Harvey P. A study of cognitive and behavioural therapy approaches to the treatment of gambling addiction. ANZCTR 2010; Vol. http://www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12610000828022.aspx.
Hodgins 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hodgins DC, Currie S, el‐Guebaly N, Peden N. Brief motivational treatment for problem gambling: a 24‐month follow‐up. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2004;18(3):293‐6. - PubMed
-
- Hodgins DC, Currie SR, el‐Guebaly N. Motivational enhancement and self‐help treatments for problem gambling. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2001;69(1):50‐7. - PubMed
Hodgins 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hodgins DC, Currie SR, el‐Guebaly N, Diskin KM. Does providing extended relapse prevention bibliotherapy to problem gamblers improve outcome?. Journal of Gambling Studies 2007;23(1):41‐54. - PubMed
Hodgins 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hodgins DC, Currie SR, Currie G, Fick GH. Randomized trial of brief motivational treatment for pathological gamblers: more is not necessarily better. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2009;77(5):950‐60. - PubMed
Korman 2008 {published data only}
-
- Korman L, Collins J, Littman‐Sharp N, Skinner W, McMain S, Mercado V. Randomized control trial of an integrated therapy for comorbid anger and gambling. Psychotherapy Research 2008;18(4):454‐65. - PubMed
McConaghy 1983 {published data only}
-
- Blaszczynski A. Clinical studies in pathological gambling: is controlled gambling an acceptable outcome?. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering 1990;51(5‐B):2609‐10.
-
- Blaszczynski A, McConaghy N, Frankova A. Control versus abstinence in the treatment of pathological gambling: a two to nine year follow‐up. British Journal of Addiction 1991;86(3):299‐306. - PubMed
-
- McConaghy N. Assessment and management of pathological gambling. British Journal of Hospital Medicine 1988;40(2):131‐6. - PubMed
-
- McConaghy N, Armstrong MS, Blaszczynski A, Allcock C. Controlled comparison of aversive therapy and imaginal desensitization in compulsive gambling. British Journal of Psychiatry 1983;142:366‐72. - PubMed
-
- McConaghy N, Blaszczynski A, Frankova A. Comparison of imaginal desensitisation with other behavioural treatments of pathological gambling. A two‐ to nine‐year follow‐up. British Journal of Psychiatry 1991;159:390‐3. - PubMed
McConaghy 1988 {published data only}
-
- McConaghy N, Armstrong MS, Blaszczynski A, Allcock C. Behavior completion versus stimulus control in compulsive gambling. Behavior Modification 1988;12(3):371‐84. - PubMed
McConaghy 1991 {published data only}
-
- McConaghy N, Blaszczynski A, Frankova A. Comparison of imaginal desensitisation with other behavioural treatments of pathological gambling: a two‐ to nine‐year follow‐up. British Journal of Psychiatry 1991;159:390‐3. - PubMed
Milton 2002 {published data only}
-
- Milton S, Crino R, Hunt C, Prosser E. The effect of compliance‐improving interventions on the cognitive‐behavioural treatment of pathological gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies 2002;18(2):207‐29. - PubMed
Myrseth 2009 {published data only}
-
- Myrseth H, Litlerè I, Støylen IJ, Pallesen S. A controlled study of the effect of cognitive‐behavioural group therapy for pathological gamblers. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 2009;63(1):22‐31. - PubMed
Petry 2005c {published data only}
-
- Petry NM. Enhanced cognitive behavior therapy for the treatment of pathological gambling. ClinicalTrials.gov 2005; Vol. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00118391.
Petry 2006b {published data only}
-
- Petry NM, Kolodner KB, Li R, Peirce JM, Roll JM, Stitzer ML, et al. Prize‐based contingency management does not increase gambling. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2006;83:269‐73. - PubMed
Petry 2008b {published data only}
-
- Petry NM. Cognitive behavioral treatments for pathological gambling. ClinicalTrials.gov 2008; Vol. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00618462.
Sani 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sani A, Carlevaro T, Ladouceur R. Impact of a counselling session on at‐risk casino patrons: a pilot study. Gambling Research 2005;17(1):47‐52.
Toneatto 2007b {published data only}
-
- Toneatto T. Development and validation of a mindfulness intervention for problem gambling: an exploratory study. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007; Vol. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00495261.
Tse 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tse S. 'XGAMBLE'‐ The effect of counselling on gambling behaviours in four New Zealand population groups. ANZCTR 2010; Vol. http://www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12610000826044.aspx.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Anonymous 2003 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Cognitive‐motivational behavior therapy for gamblers. ClinicalTrials.gov 2004; Vol. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00069420.
Anonymous 2004 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Indicated prevention with at‐risk gamblers. ClinicalTrials.gov 2004; Vol. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00078273.
Cunningham 2012 {published data only}
Petry 2008c {published data only}
-
- Petry NM. A pilot SMART design for pathological gamblers. ClinicalTrials.gov 2008; Vol. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00685724.
References to ongoing studies
Bellringer 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bellringer M, Abbott M. Effectiveness study of problem gambling standard and brief interventions. ANZCTR 2009; Vol. http://www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12609000560291.aspx.
Ciesielski 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ciesielski EM. Brief therapies for problem gambling substance abusers. ClinicalTrials.gov 2008; Vol. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00685048.
Additional references
Abbott 2006
-
- Abbott MW, Volberg RA. The measurement of adult problem and pathological gambling. International Gambling Studies 2006;6(2):175‐200.
Achab 2011
-
- Achab S, Khazaal Y. Psychopharmacological treatment in pathological gambling: a critical review. Current Pharmaceutical Design 2011;17(14):1389‐95. - PubMed
Altman 1996
Anderson 2011
APA 2000
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM‐IV. 4th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
Babor 1994
-
- Babor TF. Avoiding the horrid and beastly sin of drunkenness: does dissuasion make a difference?. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1994;62(6):1127‐40. - PubMed
Beck 1996
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Ball R, Ranieri W. Comparison of Beck Depression Inventories ‐IA and ‐II in psychiatric outpatients. Journal of Personality Assessment 1996;67(3):588‐97. - PubMed
Bergler 1957
-
- Bergler E. The Psychology of the Gambler. New York: International University Press, 1957.
Blaszczynski 2002
-
- Blaszczynski A, Nower L. A pathways model of problem and pathological gambling. Addiction 2002;97(5):487‐99. - PubMed
Brewer 2008
-
- Brewer JA, Grant JE, Potenza MN. The treatment of pathological gambling. Addictive Disorders & Their Treatment 2008;7(1):1‐13.
Burke 2003
-
- Burke BL, Arkowitz H, Menchola M. The efficacy of motivational interviewing: a meta‐analysis of controlled clinical trials. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2003;71(5):843‐61. - PubMed
Centre for Clinical Effectiveness 2010
-
- Centre for Clinical Effectiveness. Critical Appraisal Templates. Melbourne, Australia: Southern Health, 2010.
Chambless 1998
-
- Chambless DL, Hollon SD. Defining empirically supported therapies. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1998;66(1):7‐18. - PubMed
Cohen 1992
-
- Cohen J. A power primer. Psychological Bulletin 1992;112(1):155‐9. - PubMed
Cox 2004
-
- Cox BJ, Enns MW, Micaud V. Comparisons between the South Oaks Gambling Screen and a DSM‐IV–based interview in a community survey of problem gambling. Canadian Journal of Psyciatry 2004;49:258‐64. - PubMed
Deeks 2008
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DF (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
Dowling 2008
-
- Dowling N, Jackson AC, Thomas SA. Behavioral interventions in the treatment of pathological gambling: a review of activity scheduling and desensitization. International Journal of Behavioral Consultation and Therapy 2008;4(2):172‐87.
Echeburua 2001
-
- Echeburua E, Fernandez‐Montalvo J, Baez C. Predictors of therapeutic failure in slot‐machine pathological gamblers following behavioural treatment. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy 2001;29:379‐83.
Ferentzy 2009
-
- Ferentzy P, Skinner W, Antze P. Gamblers Anonymous and the 12 Steps: how an informal society has altered a recovery process in accordance with the special needs of problem gamblers. Journal of Gambling Issues 2009;23:42‐65.
Ferris 2001
-
- Ferris J, Wynne H. The Canadian Problem Gambling Index. Ottowa: Canadian Centre on Substance Abuse, 2001.
Gainsbury 2011
-
- Gainsbury S, Blaszczynski A. A systematic review of Internet‐based therapy for the treatment of addictions. Clinical Psychology Review 2011;31:490‐8. - PubMed
Gerstein 1999
-
- Gerstein D, Murphy S, Toce M, Hoffman J, Palmer, A, Johnson R, et al. Gambling Impact and Behavior Study: Report to the National Gambling Impact Study Commission. Chicago: National Opinion Research Center, 1999.
Gooding 2009
-
- Gooding P, Tarrier N. A systematic review and meta‐analysis of cognitive‐behavioural interventions to reduce problem gambling: hedging our bets?. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2009;47:592‐607. - PubMed
GRADE Working Group 2004
Grant 2004
-
- Grant JE, Steinberg MA, Kim SW, Rounsaville BJ, Potenza MN. Preliminary validity and reliability testing of a structured clinical interview for pathological gambling. Psychiatry Research 2004;128:79‐88. - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Hamilton 1959
-
- Hamilton M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. British Journal of Medical Psychology 1959;32:50‐5. - PubMed
Hamilton 1960
Henry 1996
-
- Henry SL. Pathological gambling: etiological considerations and treatment efficacy of eye movement desensitization/reprocessing. Journal of Gambling Studies 1996;12(4):395‐405. - PubMed
Hettema 2005
-
- Hettema J, Steele J, Miller WR. Motivational Interviewing. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology 2005;1(1):91‐111. - PubMed
Higgins 2008a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
Higgins 2008b
Higgins 2008c
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altmanm DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
Hodgins 2011
-
- Hodgins DC, Stea JN, Grant JE. Gambling disorders. Lancet 2011;378(9806):1874‐84. - PubMed
Huedo‐Medina 2006
-
- Huedo‐Medina T, Sanchez‐Meca J, Marin‐Martinez F, Botella J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta‐analysis: Q statistic or I2 index?. Centre for Health, Intervention, and Prevention (CHIP) Documents 2006; Vol. Paper 19. - PubMed
Hunter 2004
-
- Hunter JE, Schmidt FL. Methods of Meta‐analysis: Correcting Error and Bias in Research Findings. 2. California: Sage Publications, 2004.
Hutton 2000
-
- Hutton JL, Williamson PR. Bias in meta‐analysis due to outcome variable selection within studies. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series C 2000;49:359‐70.
Johansson 2009
-
- Johansson A, Grant JE, Kim SW, Odlaug BL, Gotestam KG. Risk factors for problematic gambling: a critical literature review. Journal of Gambling Studies 2009;25(1):67‐92. - PubMed
Juni 1999
-
- Juni P, Witschi A, Bloch R, Egger M. The hazards of scoring the quality of clinical trials for meta‐analysis. JAMA 1999;282:1054‐60. - PubMed
Kim 2009
Ladouceur 1996
-
- Ladouceur R, Walker M. A cognitive perspective on gambling. In: Sekovskis PM editor(s). Trends in Cognitive and Behavioural Therapies. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 1996:89‐98.
Leibetseder 2011
-
- Leibetseder M, Laireiter A, Vierhauser M, Hittenberger B. Efficacy and effectiveness of psychological and psycho‐pharmacological treatments in pathological gambling ‐ a meta‐analysis [Die wirksamkeit psychologischer und psychopharmakologischer interventionen bei pathologischem gluckspiel ‐ eine metaanalyse]. SUCHT 2011;57(4):275‐85.
Lesieur 1987
-
- Lesieur HR, Blume SB. The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS): a new instrument for the identification of pathological gamblers. American Journal of Psychiatry 1987;144(9):1184‐8. - PubMed
Lesieur 1992
-
- Lesieur HR, Blume SB. Modifying the Addiction Severity Index for use with pathological gamblers. American Journal on Addictions 1992;1(3):240‐7.
Lipsey 2001
-
- Lipsey MW, Wilson DB. Practical Meta‐Analysis. Vol. 49, California: Sage Publications, 2001.
Lopez Viets 1997
-
- Lopez Viets VC, Miller WR. Treatment approaches for pathological gamblers. Clinical Psychology Review 1997;17(7):689‐702. - PubMed
Lorains 2011
-
- Lorains F, Cowlishaw S, Thomas S. Prevalence of comorbid disorders in problem and pathological gambling: systematic review and meta‐analysis of population surveys. Addiction 2011;106(3):490‐8. - PubMed
Melville 2000a
-
- Melville CL, Davis CS, Matzenbacher DL. Three‐step Treatment for Problem Gambling Using Node‐link Mapping. Lake Charles, LA: McNeese State University, 2000.
Melville 2000b
-
- Melville CL. Twelve Step Facilitation Therapy Manual: Modified for the Treatment of Pathological Gambling. Lake Charles, LA: McNeese State University, 2000.
Miller 1983
-
- Miller WR. Motivational interviewing with problem drinkers. Behavioural Psychotherapy 1983;11:147‐72.
Miller 2002
-
- Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People for Change. 2. New York: The Guilford Press, 2002.
Miller 2009
Milosevic 2010
-
- Milosevic A, Ledgerwood DM. The subtyping of pathological gambling: a comprehensive review. Clinical Psychology Review 2010;30(8):988‐98. - PubMed
Mohr 2009
-
- Mohr DC, Spring B, Freedland KE, Beckner V, Arean P, Hollon SD, et al. The selection and design of control conditions for randomized controlled trials of psychological interventions. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics 2009;78:275‐84. - PubMed
Montori 2002
-
- Montori VM, Bhandari M, Devereaux PJ, Manns BJ, Ghali WA, Guyatt GH. In the dark: the reporting of blinding status in randomized controlled trials. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2002;55:787‐90. - PubMed
Normand 1999
-
- Normand ST. Meta‐analysis: formulating, evaluating, combining, and reporting. Statistics in Medicine 1998;18:321‐59. - PubMed
Ortiz 2006
-
- Ortiz L. CBT for Pathological Gambling. Stockholm: Natur & Kultur, 2006.
Pallanti 2005
-
- Pallanti S, DeCaria C, Grant JE, Urpe M, Hollander E. Reliability and validity of the pathological gambling adaptation of the Yale‐Brown Obsessive‐Compulsive Scale (PG‐YBOCS). Journal of Gambling Studies 2005;21(4):431‐43. - PubMed
Pallesen 2005
-
- Pallesen S, Mitsem M, Kvale G, Johnsen B, Molde H. Outcome of psychological treatments of pathological gambling. Addiction 2005;100:1412‐22. - PubMed
Petry 2003
-
- Petry NM. A comparison of treatment‐seeking pathological gamblers based on preferred gambling activity. Addiction 2003;98(5):645‐55. - PubMed
Petry 2005a
-
- Petry NM. Gamblers Anonymous and cognitive‐behavioral therapies for pathological gamblers. Journal of Gambling Studies 2005;21(1):27‐33. - PubMed
Petry 2005b
-
- Petry NM. Pathological Gambling: Etiology, Comorbidity and Treatments. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association Press, 2005.
Petry 2010
-
- Petry NM. Pathological gambling and the DSM‐V. International Gambling Studies 2010;10(2):113‐5.
PGRTC 2011
-
- Problem Gambling Research and Treatment Centre (PGRTC). Guideline for Screening, Assessment and Treatment in Problem Gambling. Clayton: Monash University, 2011.
Proudfoot 2004
-
- Proudfoot JG. Computer‐based treatment for anxiety and depression: Is it feasible? Is it effective?. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 2004;28(3):353‐63. - PubMed
Raylu 2010
-
- Raylu N, Oei TP. A Cognitive Behavioural Therapy Programme for Problem Gambling: Therapist Manual. Hoboken: Routledge, 2010.
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Schulz 2002
-
- Schulz KF, Grimes DA. Allocation concealment in randomised trials: defending against deciphering. Lancet 2002;359(9306):614‐8. - PubMed
Shaffer 1994
-
- Shaffer HJ, LaBrie R, Scanlan KM, Cummings TN. Pathological gambling among adolescents: Massachusetts Gambling Screen (MAGS). Journal of Gambling Studies 1994;10(4):339‐62. - PubMed
Shaffer 2002
-
- Shaffer HK, Korn DA. Gambling and related mental disorders: a public health analysis. Annual Review of Public Health 2002;23:171‐212. - PubMed
Sharpe 1993
-
- Sharpe L, Tarrier N. Towards a cognitive‐behavioural theory of problem gambling. British Journal of Psychiatry 1993;162:407‐12. - PubMed
Sharpe 2002
-
- Sharpe L. A reformulated cognitive‐behavioral model of problem gambling: a biopsychosocial perspective. Clinical Psychology Review 2002;22(1):1‐25. - PubMed
Shih 2002
Slutske 2006
-
- Slutske WS. Natural recovery and treatment‐seeking in pathological gambling: results of two U.S. national surveys. American Journal of Psychiatry 2006;163(2):297‐302. - PubMed
Sobell 1992
-
- Sobell LC, Sobell MB. Timeline Follow‐back: a technique for assessing self‐reported ethanol consumption. In: Allen J, Litten RZ editor(s). Measuring Alcohol Consumption: Psychosocial and Biological Methods. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 1992:41‐72.
Spielberger 1970
-
- Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, Lushene RE. Manual for the State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press, 1970.
Sterne 2008
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D. Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
Stewart 2008
-
- Stewart SH, Zack M, Collins P, Klein RM, Fragopoulos F. Subtypting pathological gamblers on the basis of affective motivations for gambling: relations to gambling problems, drinking problems, and affective motivations for drinking. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2008;22(2):257‐68. - PubMed
Stinchfield 2004
-
- Stinchfield RS, Govoni R, Frisch GR. Screening and assessment instruments. In: Grant JE, Potenza MN editor(s). Pathological Gambling: A Clinical Guide to Treatment. Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc., 2004:207‐31.
Toneatto 1999
-
- Toneatto T. Cognitive psychopathology of problem gambling. Substance Use and Misuse 1999;34:1593‐604. - PubMed
Toneatto 2003
-
- Toneatto T, Ladouceur R. Treatment of pathological gambling: a critical review of the literature. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2003;17(4):284‐92. - PubMed
Toneatto 2007a
-
- Toneatto T, Nguyen L. Individual characteristics and problem gambling behavior. In: Smith G, Hodgins D, Williams R editor(s). Research and Measurement Issues in Gambling Studies. Toronto: Elsevier, 2007:280‐95.
VGDHS 2000
-
- Victorian Government Department of Human Services. Playing for Time: Exploring the Impacts of Gambling on Women. Melbourne: Author, 2000.
Volberg 2006
-
- Volberg RA, Nysse‐Carris KL, Gerstein DR. 2006 California Problem Gambling Prevalence Survey. Office of Problem and Pathological Gambling, Californian Department of Alcohol and Drug Programs 2006.
Walker 2006
-
- Walker M, Toneatto T, Potenza MN, Petry N, Ladouceur R, Hodgins DC, et al. A framework for reporting outcomes in problem gambling treatment research: The Banff, Alberta consensus. Addiction 2006;101(4):504‐11. - PubMed
Wardle 2010
-
- Wardle H, Moody A, Spence S, Orford J, Volberg R, Jotangia O, et al. British Gambling Prevalence Survey 2010. National Centre for Social Research 2010.
Westphal 2007
-
- Westphal J. Are the effects of gambling treatment overestimated?. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction 2007;5(1):65‐79.
Westphal 2008
-
- Westphal JR. How well are we helping problem gamblers? An update of the evidence base supporting problem gambling treatment. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction 2008;6(3):249‐64.
Wood 2004
-
- Wood AM, White IR, Thompson SG. Are missing outcome data adequately handled? A review of published randomized controlled trials in major medical journals. Clinical Trials 2004;1:368‐76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

