Whole-genome microRNA screening identifies let-7 and mir-18 as regulators of germ layer formation during early embryogenesis
- PMID: 23152446
- PMCID: PMC3521625
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.200758.112
Whole-genome microRNA screening identifies let-7 and mir-18 as regulators of germ layer formation during early embryogenesis
Abstract
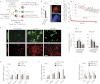
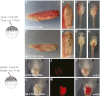
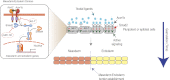
Tight control over the segregation of endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm is essential for normal embryonic development of all species, yet how neighboring embryonic blastomeres can contribute to different germ layers has never been fully explained. We postulated that microRNAs, which fine-tune many biological processes, might modulate the response of embryonic blastomeres to growth factors and other signals that govern germ layer fate. A systematic screen of a whole-genome microRNA library revealed that the let-7 and miR-18 families increase mesoderm at the expense of endoderm in mouse embryonic stem cells. Both families are expressed in ectoderm and mesoderm, but not endoderm, as these tissues become distinct during mouse and frog embryogenesis. Blocking let-7 function in vivo dramatically affected cell fate, diverting presumptive mesoderm and ectoderm into endoderm. siRNA knockdown of computationally predicted targets followed by mutational analyses revealed that let-7 and miR-18 down-regulate Acvr1b and Smad2, respectively, to attenuate Nodal responsiveness and bias blastomeres to ectoderm and mesoderm fates. These findings suggest a crucial role for the let-7 and miR-18 families in germ layer specification and reveal a remarkable conservation of function from amphibians to mammals.
Figures




References
-
- Armes NA, Smith JC 1997. The ALK-2 and ALK-4 activin receptors transduce distinct mesoderm-inducing signals during early Xenopus development but do not co-operate to establish thresholds. Development 124: 3797–3804 - PubMed
-
- Branford WW, Yost HJ 2002. Lefty-dependent inhibition of Nodal- and Wnt-responsive organizer gene expression is essential for normal gastrulation. Curr Biol 12: 2136–2141 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
