The role of PR-Set7 in replication licensing depends on Suv4-20h
- PMID: 23152447
- PMCID: PMC3521623
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.195636.112
The role of PR-Set7 in replication licensing depends on Suv4-20h
Abstract
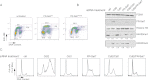
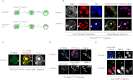
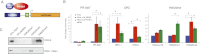
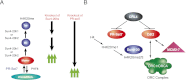
PR-Set7 is the sole monomethyltransferase responsible for H4K20 monomethylation (H4K20me1) that is the substrate for further methylation by Suv4-20h1/h2. PR-Set7 is required for proper cell cycle progression and is subject to degradation by the CRL4(Cdt2) ubiquitin ligase complex as a function of the cell cycle and DNA damage. This report demonstrates that PR-Set7 is an important downstream effector of CRL4(Cdt2) function during origin of DNA replication licensing, dependent on Suv4-20h1/2 activity. Aberrant rereplication correlates with decreased levels of H4K20me1 and increased levels of H4K20 trimethylation (H4K20me3). Expression of a degradation-resistant PR-Set7 mutant in the mouse embryo that is normally devoid of Suv4-20 does not compromise development or cell cycle progression unless Suv4-20h is coexpressed. PR-Set7 targeting to an artificial locus results in recruitment of the origin recognition complex (ORC) in a manner dependent on Suv4-20h and H4K20me3. Consistent with this, H4K20 methylation status plays a direct role in recruiting ORC through the binding properties of ORC1 and ORCA/LRWD1. Thus, coordinating the status of H4K20 methylation is pivotal for the proper selection of DNA replication origins in higher eukaryotes.
Figures

References
-
- Anastassiadis K, Kim J, Daigle N, Sprengel R, Scholer HR, Stewart AF 2002. A predictable ligand regulated expression strategy for stably integrated transgenes in mammalian cells in culture. Gene 298: 159–172 - PubMed
-
- Arias EE, Walter JC 2007. Strength in numbers: Preventing rereplication via multiple mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. Genes Dev 21: 497–518 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
