Aberrant overexpression of IL-15 initiates large granular lymphocyte leukemia through chromosomal instability and DNA hypermethylation
- PMID: 23153537
- PMCID: PMC3627362
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.09.009
Aberrant overexpression of IL-15 initiates large granular lymphocyte leukemia through chromosomal instability and DNA hypermethylation
Abstract
How inflammation causes cancer is unclear. Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine elevated in human large granular lymphocyte (LGL) leukemia. Mice overexpressing IL-15 develop LGL leukemia. Here, we show that prolonged in vitro exposure of wild-type (WT) LGL to IL-15 results in Myc-mediated upregulation of aurora kinases, centrosome aberrancies, and aneuploidy. Simultaneously, IL-15 represses miR-29b via induction of Myc/NF-κBp65/Hdac-1, resulting in Dnmt3b overexpression and DNA hypermethylation. All this is validated in human LGL leukemia. Adoptive transfer of WT LGL cultured with IL-15 led to malignant transformation in vivo. Drug targeting that reverses miR-29b repression cures otherwise fatal LGL leukemia. We show how excessive IL-15 initiates cancer and demonstrate effective drug targeting for potential therapy of human LGL leukemia.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
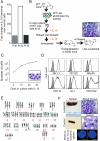
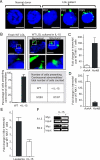

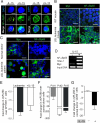
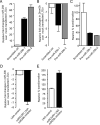

Comment in
-
Does IL-15 have a causative role in large granular lymphocyte leukemia?Immunotherapy. 2013 Mar;5(3):231-4. doi: 10.2217/imt.13.7. Immunotherapy. 2013. PMID: 23444952
References
-
- Aboud M, Golde DW, Bersch N, Rosenblatt JD, Chen IS. A colony assay for in vitro transformation by human T cell leukemia viruses type I and type II. Blood. 1987;70:432–436. - PubMed
-
- Asadullah K, Haeussler-Quade A, Gellrich S, Hanneken S, Hansen-Hagge TE, Docke WD, Volk HD, Sterry W. IL-15 and IL-16 overexpression in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas: stage-dependent increase in mycosis fungoides progression. Exp Dermatol. 2000;9:248–251. - PubMed
-
- Azimi N, Jacobson S, Leist T, Waldmann TA. Involvement of IL-15 in the pathogenesis of human T lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: implications for therapy with a monoclonal antibody directed to the IL-2/15R beta receptor. J Immunol. 1999;163:4064–4072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA149623/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68458/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA068458/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA149623/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA09338/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA095426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA068458/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA140158/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA102031/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA140158/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA102031/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA95426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009338/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

