Amyloid formation in heterogeneous environments: islet amyloid polypeptide glycosaminoglycan interactions
- PMID: 23154166
- PMCID: PMC3753189
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.11.003
Amyloid formation in heterogeneous environments: islet amyloid polypeptide glycosaminoglycan interactions
Abstract
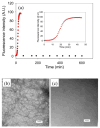
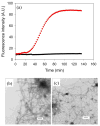
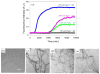
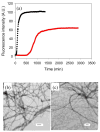
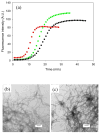
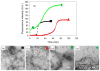
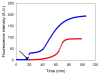
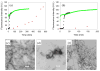
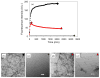
Amyloid formation plays an important role in a broad range of diseases, and the search for amyloid inhibitors is an active area of research. Amyloid formation takes places in a heterogeneous environment in vivo with the potential for interactions with membranes and with components of the extracellular matrix. Naturally occurring amyloid deposits are associated with sulfated proteoglycans and other factors. However, the vast majority of in vitro assays of amyloid formation and amyloid inhibition are conducted in homogeneous solution where the potential for interactions with membranes or sulfated proteoglycans is lacking and it is possible that different results may be obtained in heterogeneous environments. We show that variants of islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), which are non-amyloidogenic in homogeneous solution, can be readily induced to form amyloid in the presence of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). GAGs are found to be more effective than anionic lipid vesicles at inducing amyloid formation on a per-charge basis. Several known inhibitors of IAPP amyloid formation are shown to be less effective in the presence of GAGs.
Copyright © 2012. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Vendruscolo M, Zurdo J, MacPhee CE, Dobson CM. Protein folding and misfolding: a paradigm of self-assembly and regulation in complex biological systems. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser A-Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003;361:1205–1222. - PubMed
-
- Sipe JD. Amyloidosis. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1994;31:325–354. - PubMed
-
- Kirkitadze MD, Bitan G, Teplow DB. Paradigm shifts in Alzheimer’s disease and other neuro degenerative disorders: The emerging role of oligomeric assemblies. J Neurosci Res. 2002;69:567–577. - PubMed
-
- Lorenzo A, Razzaboni B, Weir GC, Yankner BA. Pancreatic islet cell toxicity of amylin associated with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1994;368:756–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

