Combination treatment with progesterone and vitamin D hormone is more effective than monotherapy in ischemic stroke: the role of BDNF/TrkB/Erk1/2 signaling in neuroprotection
- PMID: 23154302
- PMCID: PMC3568940
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.10.004
Combination treatment with progesterone and vitamin D hormone is more effective than monotherapy in ischemic stroke: the role of BDNF/TrkB/Erk1/2 signaling in neuroprotection
Abstract
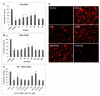
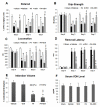
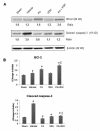
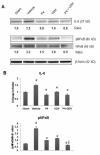
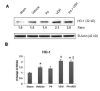
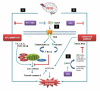
We investigated whether combinatorial post-injury treatment with progesterone (P4) and vitamin D hormone (VDH) would reduce ischemic injury more effectively than P4 alone in an oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD) model in primary cortical neurons and in a transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) model in rats. In the OGD model, P4 and VDH each showed neuroprotection individually, but combination of the "best" doses did not show substantial efficacy; instead, the lower dose of VDH in combination with P4 was the most effective. In the tMCAO model, P4 and VDH were given alone or in combination at different times post-occlusion for 7 days. In vivo data confirmed the in vitro findings and showed better infarct reduction at day 7 and functional outcomes (at 3, 5 and 7 days post-occlusion) after combinatorial treatment than when either agent was given alone. VDH, but not P4, upregulated heme oxygenase-1, suggesting a pathway for the neuroprotective effects of VDH differing from that of P4. The combination of P4 and VDH activated brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its specific receptor, tyrosine kinase receptor-B. Under specific conditions VDH potentiates P4's neuroprotective efficacy and should be considered as a potential partner of P4 in a low-cost, safe and effective combinatorial treatment for stroke.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
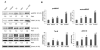
References
-
- Abe K, Hayashi T. Expression of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene in rat brain after transient MCA occlusion. Brain Res. 1997;776:230–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

