SEL-10/Fbw7-dependent negative feedback regulation of LIN-45/Braf signaling in C. elegans via a conserved phosphodegron
- PMID: 23154983
- PMCID: PMC3505822
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.203703.112
SEL-10/Fbw7-dependent negative feedback regulation of LIN-45/Braf signaling in C. elegans via a conserved phosphodegron
Abstract
The conserved E3 ubiquitin ligase component named SEL-10 in Caenorhabditis elegans and Fbw7 in mammals targets substrates for ubiquitin-mediated degradation through a high-affinity binding site called a Cdc4 phosphodegron (CPD). As many known substrates of Fbw7 are oncoproteins, the identification of new substrates may offer insight into cancer biology as well as aspects of proteome regulation. Here, we evaluated whether the presence of an evolutionarily conserved CPD would be a feasible complement to proteomics-based approaches for identifying new potential substrates. For functional assessments, we focused on LIN-45, a component of the signal transduction pathway underlying vulval induction and the ortholog of human Braf, an effector of Ras in numerous cancers. Our analysis demonstrates that LIN-45 behaves as a bona fide substrate of SEL-10, with mutation of the CPD or loss of sel-10 resulting in increased activity and protein stability in vivo. Furthermore, during vulval induction, the downstream kinase MPK-1/ERK is also required for LIN-45 protein degradation in a negative feedback loop, resulting in degradation of LIN-45 where ERK is highly active. As the CPD consensus sequence is conserved in human Braf, we propose that Fbw7 may also regulate Braf stability in some cell contexts. We discuss the implications of our findings for vulval development in C. elegans, the potential applicability to human Braf, and the value of a CPD-based predictive approach for human Fbw7 substrates.
Figures




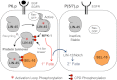
References
-
- Akhoondi S, Sun D, von der Lehr N, Apostolidou S, Klotz K, Maljukova A, Cepeda D, Fiegl H, Dafou D, Marth C, et al. 2007. FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer Res 67: 9006–9012 - PubMed
-
- Berset T, Hoier EF, Battu G, Canevascini S, Hajnal A 2001. Notch inhibition of RAS signaling through MAP kinase phosphatase LIP-1 during C. elegans vulval development. Science 291: 1055–1058 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
