ras-Induced up-regulation of CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase α contributes to malignant transformation of intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 23155050
- PMCID: PMC3537062
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.347682
ras-Induced up-regulation of CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase α contributes to malignant transformation of intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
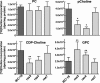
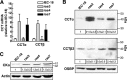
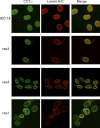
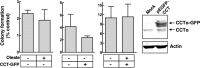
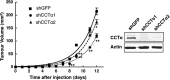
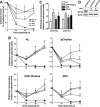
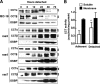
Cancer cells have enhanced lipogenic capacity characterized by increased synthesis of fatty acids and complex lipids, including phosphatidylcholine (PC). As the rate-limiting enzyme in the CDP-choline pathway for PC synthesis, CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase α (CCTα) is implicated in the provision of membranes and bioactive lipids necessary of cell proliferation. In this study, we assessed the role of CCTα in malignant intestinal epithelial cells transformed with activated H-ras (IEC-ras). Three IEC-ras clones had significant up-regulation CCTα expression, but PC synthesis and in vitro activity of CCTα were similar to control IEC. RNA interference of CCTα in adherent IEC-ras did not affect PC synthesis, confirming that the enzyme was relatively inactive. However, CCTα silencing in ras-transformed IEC reduced anchorage-independent growth, a criterion for malignant transformation, as well as tumorigenicity in mice. Relative to their adherent counterparts, detached IEC-ras had increased PC synthesis that was attenuated by inducible CCTα silencing. Detachment of IEC-ras was accompanied by increased CCTα phosphorylation and cytosolic enzyme activity. We conclude that the expanded pool of CCTα in IEC-ras is activated by detachment. This provides the increased PC biosynthetic capacity that contributes to malignant transformation of intestinal epithelial cells when detached from the extracellular matrix.
Figures



References
-
- Hsu P. P., Sabatini D. M. (2008) Cancer cell metabolism. Warburg and beyond. Cell 134, 703–707 - PubMed
-
- Menendez J. A., Lupu R. (2007) Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 763–777 - PubMed
-
- Bauer D. E., Hatzivassiliou G., Zhao F., Andreadis C., Thompson C. B. (2005) ATP citrate lyase is an important component of cell growth and transformation. Oncogene 24, 6314–6322 - PubMed
-
- Hatzivassiliou G., Zhao F., Bauer D. E., Andreadis C., Shaw A. N., Dhanak D., Hingorani S. R., Tuveson D. A., Thompson C. B. (2005) ATP citrate lyase inhibition can suppress tumor cell growth. Cancer Cell 8, 311–321 - PubMed
-
- Brusselmans K., De Schrijver E., Verhoeven G., Swinnen J. V. (2005) RNA interference-mediated silencing of the acetyl-CoA-carboxylase-α gene induces growth inhibition and apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 65, 6719–6725 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

