VEGF -634C/G genotype is predictive of long-term survival after treatment with a definitive 5-fluorouracil/cisplatin-based chemoradiotherapy in Japanese patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 23155356
- PMCID: PMC3498747
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.4914
VEGF -634C/G genotype is predictive of long-term survival after treatment with a definitive 5-fluorouracil/cisplatin-based chemoradiotherapy in Japanese patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Reports have been accumulating that genetic properties are predictive of clinical response after and/or toxicity during cancer chemotherapy, but little information is available concerning effects on long-term survival. In this study, 49 Japanese patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) were followed up for 5 years after treatment with a definitive 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)/cisplatin (CDDP)-based chemoradiotherapy (CRT), and the effects of genotypes of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were retrospectively revaluated in terms of prediction of long-term survival.
Methods: A course consisted of the continuous infusion of 5-FU at 400 mg/m(2)/day for days 1-5 and 8-12, the infusion of CDDP at 40 mg/m(2)/day on days 1 and 8, and radiation at 2 Gy/day on days 1 to 5, 8 to 12, and 15 to 19, with a second course repeated after a 2-week interval. The VEGF genotypes -1498T/C, -1154G/A, -634C/G, -7C/T, 936C/T, and 1612G/A were evaluated.
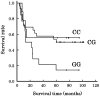
Results: The complete response (CR) rate was 46.9% (23/49). The 5-year survival rate was 42.9 % (21/49). There were 7 patients with a CR, but survival of less than 5 years. They died from myocardial infarction (N=1), sudden cardiac death after suffering from heart failure (N=1), acute myeloid leukemia that developed from myelodysplastic syndromes (N=1), factors not specified (N=2), oropharynx cancer (N=1), and tongue cancer (N=1). VEGF -634C/G had no effect on clinical response, but long-term survival depended on the genotype (p=0.033, Fisher's; p=0.038, Cochran-Armitage; p=0.079, Log-rank). The genotype frequency of 7 patients with a CR, but survival of less than 5 years was different from that for the other 42 patients (p=0.032, Fisher's). None of the other 5 genotypes evaluated affected either clinical response or survival.
Conclusions: VEGF -634C/G is possibly predictive of long-term survival after treatment with a definitive 5-FU/CDDP-based CRT. Further clinical studies with a larger number of cases are needed to clarify the effects of this genotype.
Keywords: chemoradiotherapy; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; late toxicity; prognosis; vascular endothelial growth factor..
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Cooper JS, Guo MD, Herskovic A. et al. Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced esophageal cancer: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized trial (RTOG 85-01). Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. JAMA. 1999;281:1623–1627. - PubMed
-
- Herskovic A, Martz K, al-Sarraf M. et al. Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in patients with cancer of the esophagus. N.Engl.J.Med. 1992;326:1593–1598. - PubMed
-
- al-Sarraf M, Martz K, Herskovic A. et al. Progress report of combined chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in patients with esophageal cancer: an intergroup study. J.Clin.Oncol. 1997;15:277–284. - PubMed
-
- Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S. et al. Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials. The CONSORT statement. JAMA. 1996;276:637–639. - PubMed
-
- Ohtsu A, Boku N, Muro K. et al. Definitive chemoradiotherapy for T4 and/or M1 lymph node squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J.Clin.Oncol. 1999;17:2915–2921. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials