Influence of chronic amphetamine treatment and acute withdrawal on serotonin synthesis and clearance mechanisms in the rat ventral hippocampus
- PMID: 23157166
- PMCID: PMC3563776
- DOI: 10.1111/ejn.12050
Influence of chronic amphetamine treatment and acute withdrawal on serotonin synthesis and clearance mechanisms in the rat ventral hippocampus
Abstract
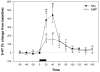
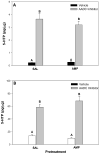
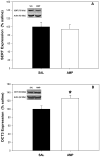
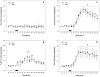
Amphetamine withdrawal in both humans and rats is associated with increased anxiety states, which are thought to contribute to drug relapse. Serotonin in the ventral hippocampus mediates affective behaviors, and reduced serotonin levels in this region are observed in rat models of high anxiety, including during withdrawal from chronic amphetamine. This goal of this study was to understand the mechanisms by which reduced ventral hippocampus serotonergic neurotransmission occurs during amphetamine withdrawal. Serotonin synthesis (assessed by accumulation of serotonin precursor as a measure of the capacity of in vivo tryptophan hydroxylase activity), expression of serotonergic transporters, and in vivo serotonergic clearance using in vivo microdialysis were assessed in the ventral hippocampus in adult male Sprague Dawley rats at 24 h withdrawal from chronic amphetamine. Overall, results showed that diminished extracellular serotonin at 24 h withdrawal from chronic amphetamine was not accompanied by a change in capacity for serotonin synthesis (in vivo tryptophan hydroxylase activity), or serotonin transporter expression or function in the ventral hippocampus, but instead was associated with increased expression and function of organic cation transporters (low-affinity, high-capacity serotonin transporters). These findings suggest that 24 h withdrawal from chronic amphetamine reduces the availability of extracellular serotonin in the ventral hippocampus by increasing organic cation transporter-mediated serotonin clearance, which may represent a future pharmacological target for reversing anxiety states during drug withdrawal.
© 2012 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serotonergic responses to stress are enhanced in the central amygdala and inhibited in the ventral hippocampus during amphetamine withdrawal.Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Dec;40(11):3684-92. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12735. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25234335 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin in the ventral hippocampus modulates anxiety-like behavior during amphetamine withdrawal.Neuroscience. 2014 Dec 5;281:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.09.019. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 25241066 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic neurotransmission in the ventral hippocampus is enhanced by corticosterone and altered by chronic amphetamine treatment.Neuroscience. 2011 May 19;182:105-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.03.020. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21420472 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and serotonergic consequences of decreasing or increasing hippocampus brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein levels in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Nov;55(6):1006-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.08.001. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18761360 Review.
-
Serotonin (5-HT) in the regulation of depression-related emotionality: insight from 5-HT transporter and tryptophan hydroxylase-2 knockout mouse models.Curr Drug Targets. 2013 May 1;14(5):549-70. doi: 10.2174/1389450111314050005. Curr Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23547810 Review.
Cited by
-
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury with Social Defeat Stress Alters Anxiety, Contextual Fear Extinction, and Limbic Monoamines in Adult Rats.Front Behav Neurosci. 2016 Apr 19;10:71. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00071. eCollection 2016. Front Behav Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27147992 Free PMC article.
-
Amphetamine Withdrawal Differentially Increases the Expression of Organic Cation Transporter 3 and Serotonin Transporter in Limbic Brain Regions.J Exp Neurosci. 2016 Jul 21;10:93-100. doi: 10.4137/JEN.S40231. eCollection 2016. J Exp Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27478387 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupting monotony during social isolation stress prevents early development of anxiety and depression like traits in male rats.BMC Neurosci. 2015 Feb 14;16:2. doi: 10.1186/s12868-015-0141-y. BMC Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25880744 Free PMC article.
-
Organic cation transporters in psychiatric and substance use disorders.Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Jan;253:108574. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108574. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38072333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonergic responses to stress are enhanced in the central amygdala and inhibited in the ventral hippocampus during amphetamine withdrawal.Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Dec;40(11):3684-92. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12735. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25234335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amphoux A, Vialou V, Drescher E, Bruss M, Mannoury La Cour C, Rochat C, Millan MJ, Giros B, Bonisch H, Gautron S. Differential pharmacological in vitro properties of organic cation transporters and regional distribution in rat brain. Neuropharmacology. 2006;50:941–952. - PubMed
-
- Azmitia EC, Segal M. An autoradiographic analysis of the differential ascending projections of the dorsal and median raphe nuclei in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1978;179:641–667. - PubMed
-
- Badoer E, Wurth H, Turck D, Qadri F, Itoi K, Dominiak P, Unger T. The K+-induced increases in noradrenaline and dopamine release are accompanied by reductions in the release of their intraneuronal metabolites from the rat anterior hypothalamus. An in vivo brain microdialysis study. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989;339:54–59. - PubMed
-
- Baganz NL, Horton RE, Calderon AS, Owens WA, Munn JL, Watts LT, Koldzic-Zivanovic N, Jeske NA, Koek W, Toney GM, Daws LC. Organic cation transporter 3: Keeping the brake on extracellular serotonin in serotonin-transporter-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:18976–18981. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

