Snail promotes an invasive phenotype in lung carcinoma
- PMID: 23157169
- PMCID: PMC3546026
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-104
Snail promotes an invasive phenotype in lung carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Snail is a transcriptional factor which is known to influence the epitheliomesenchymal transition (EMT) by regulating adhesion proteins such as E-cadherin and claudins as well as matrix metalloproteases (MMP).
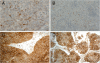
Methods: To evaluate the functional importance of snail, a transciptional factor involved in EMT in lung tumors, we investigated its expression in a large set of lung carcinomas by immunohistochemistry. Expression of snail and effects of snail knockdown was studied in cell lines.
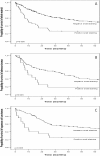
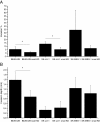
Results: Nuclear snail expression was seen in 21% of cases this being strongest in small cell lung carcinomas (SCLC). There was significantly greater snail expression in SCLC compared to squamous cell or adenocarcinoma. Positive snail expression was associated with poor survival in the whole material and separately in squamous cell and adenocarcinomas. In Cox regression analysis, snail expression showed an independent prognostic value in all of these groups. In several cell lines knockdown of snail reduced invasion in both matrigel assay and in the myoma tissue model for invasion. The influence of snail knockdown on claudin expression was cell type specific. Snail knockdown in these cell lines modified the expression of MMP2 and MMP9 but did not influence the activation of these MMPs to any significant degree.
Conclusions: The results show that snail plays an important role in the invasive characteristics of lung carcinoma influencing the survival of the patients. Snail knockdown might thus be one option for targeted molecular therapy in lung cancer. Snail knockdown influenced the expression of claudins individually in a cell-line dependent manner but did not influence MMP expressions or activations to any significant degree.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Slug is associated with poor survival in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Aug 15;7(9):5846-54. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25337226 Free PMC article.
-
Snail-associated epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma motility and progression.J Pathol. 2008 Jul;215(3):330-9. doi: 10.1002/path.2365. J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18491351
-
Increased invasion and matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression by Snail-induced mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinomas.Int J Oncol. 2003 Apr;22(4):891-8. Int J Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12632084
-
[Expression and significance of Snail and Claudin-3 in non-small cell lung cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2012 Oct;15(10):583-90. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2012.10.04. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23075682 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, TWIST1 and Snail expression in resectable non-small cell lung cancer.Thorax. 2009 Dec;64(12):1082-9. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.115691. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Thorax. 2009. PMID: 19778933 Review.
Cited by
-
Activating Invasion and Metastasis in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Role of the Tumour Immune Microenvironment and Mechanisms of Vasculogenesis, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Cell Migration, and Organ Tropism.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Oct;7(10):e70018. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.70018. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 39376011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardamonin Inhibits Metastasis of Lewis Lung Carcinoma Cells by Decreasing mTOR Activity.PLoS One. 2015 May 21;10(5):e0127778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127778. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25996501 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1: A small fox that makes more tracks for cancer progression and metastasis.Semin Cancer Biol. 2023 Jul;92:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.03.007. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Semin Cancer Biol. 2023. PMID: 36958703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase D2 induces invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating matrix metalloproteinases.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Feb;25(3):324-36. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-06-0334. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24336522 Free PMC article.
-
FOXK1, Regulated by miR-365-3p, Promotes Cell Growth and EMT Indicates Unfavorable Prognosis in Breast Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jan 21;13:623-634. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S212702. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32021304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guaita S, Puig I, Franci C, Garrido M, Dominguez D, Batlle E, Sancho E, Dedhar S, De Herreros AG, Baulida J. Snail induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in tumor cells is accompanied by MUC1 repression and ZEB1 expression. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:39209–39216. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206400200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

