Plasma acetylcholinesterase activity correlates with intracerebral β-amyloid load
- PMID: 23157337
- PMCID: PMC3768143
Plasma acetylcholinesterase activity correlates with intracerebral β-amyloid load
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have demonstrated alterations in the peripheral cholinergic system in Alzheimer's disease (AD), though results have been inconsistent and not linked to in vivo biomarkers of pathology. We examined the relationship between amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques and plasma cholinesterase activity in a heterogeneous dementia population.
Methods: 29 participants with clinical AD and 35 with non-AD diagnoses underwent positron emission tomography (PET) with the amyloid ligand [11C] PIB and plasma measurements of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) activity. Multi-linear regression was used to evaluate the relationship between AChE or BChE activity and PIB binding (adjusted for age, sex, apolipoprotein E4 and vascular risk), applying voxel-wise and region of interest (ROI) approaches. AChE activity was further adjusted for cholinesterase inhibitor (ChE-I) use. Global amyloid load was measured using a PIB Index, representing mean tracer binding in frontal, parietal, lateral temporal and cingulate cortex.
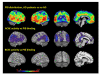
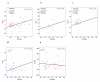
Results: AChE activity was correlated with PIB Index (β=0.39, p < 0.001) and with regional PIB binding in frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes, precuneus and posterior cingulate on both voxel-wise (p < 0.001 uncorrected) and ROI (β=0.26-0.41, p < 0.005) analysis. Correlations remained significant after covarying clinical diagnosis (β=0.42, p=0.001), and among participants naive to ChE-I (β=0.51, p=0.005). No correlation was found between BChE activity and PIB. Among AD participants, disease severity was not correlated with AChE, BChE or PIB Index.
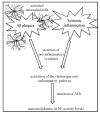
Conclusion: AChE activity in plasma is correlated with brain Aβ load. Activation of the 'anti-inflammatory cholinergic pathway' may provide the link between Aβ plaques and peripheral cholinergic measures.
Figures
References
-
- The National Institute on Aging, and Reagan Institute Working Group on Diagnostic Criteria for the Neuropathological Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18:S1–2. - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT, Dean RL, 3rd, Beer B, Lippa AS. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science. 1982 Jul 30;217(4558):408–14. - PubMed
-
- Coyle JT, Price DL, DeLong MR. Alzheimer’s disease: A disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1184–90. - PubMed
-
- Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Bennett DA, Craft S, Fagan AM, Iwatsubo T, et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011 May;7(3):280–92. Epub 2011 Apr 21. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

