An emerging role for microRNAs in NF1 tumorigenesis
- PMID: 23158014
- PMCID: PMC3537581
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-7364-6-23
An emerging role for microRNAs in NF1 tumorigenesis
Abstract
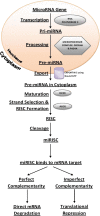
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNA, which have recently been shown to have a wide variety of regulatory functions in relation to gene expression. Since their identification nearly 20 years ago, miRNAs have been found to play an important role in cancer, including in neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)-associated tumours. NF1 is the most commonly inherited tumour predisposition syndrome and can lead to malignancy via the development of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours (MPNSTs). Although the mechanisms by which benign neurofibromas develop into MPNSTs still remain to be elucidated, it is becoming increasingly clear that miRNAs play a key role in this process and have the potential to be used as both diagnostic and prognostic markers of tumorigenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2001;431:350–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

