Multiple environmental chemical exposures to lead, mercury and polychlorinated biphenyls among childbearing-aged women (NHANES 1999-2004): Body burden and risk factors
- PMID: 23158727
- PMCID: PMC3578119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2012.10.005
Multiple environmental chemical exposures to lead, mercury and polychlorinated biphenyls among childbearing-aged women (NHANES 1999-2004): Body burden and risk factors
Abstract
Background: Lead, mercury and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are neurotoxicants with intergenerational health consequences from maternal body burden and gestational exposures. Little is known about multiple chemical exposures among childbearing-aged women.
Objectives: To determine the percentage of women aged 16-49 of diverse races and ethnicities whose body burdens for all three xenobiotics were at or above the median; to identify mixed exposures; and to describe those women disproportionately burdened by two or more of these chemicals based on susceptibility- and exposure-related attributes, socioeconomic factors and race-ethnicity.
Methods: Secondary data analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1999-2004).
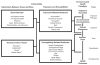
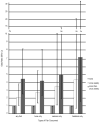
Results: The best-fit logistic regression model without interactions contained 12 variables. Four risk factors associated with body burden were notable (P≤0.05). An exponential relationship was demonstrated with increasing age. Any fish consumption in past 30 days more than doubled the odds. Heavy alcohol consumption increased the relative risk. History of breastfeeding reduced this risk. These women were more likely to have two xenobiotics at or above the median than one. More than one-fifth of these childbearing-aged women had three xenobiotic levels at or above the median.
Conclusions: These findings are among the first description of US childbearing-aged women's body burden and risk factors for multiple chemical exposures. This study supports increasing age, any fish consumption and heavy alcohol consumption as significant risk factors for body burden. History of breastfeeding lowered the body burden. Limited evidence was found of increased risk among minority women independent of other risk factors.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) Interaction Profile for Persistent Chemicals Found in Breast Milk (Chlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins, Hexachlorobenzene, p,p′-DDE, Methylmercury, and Polychlorinated Biphenyls) Author; Atlanta, GA: 2004. - PubMed
-
- Axelrad DA, Goodman S, Woodruff T. PCB body burden in U.S. women of childbearing age 2001–2002: an evaluation of alternate summary metrics of NHANES data. Environ Res. 2009;109:368–378. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2009.01.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

