Plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma, a chemosensitive cancer with poor prognosis, and peritoneal carcinomatosis
- PMID: 23159581
- PMCID: PMC4243847
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.11.084
Plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma, a chemosensitive cancer with poor prognosis, and peritoneal carcinomatosis
Abstract
Purpose: Plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma is a rare variant histology with poorly defined clinical behavior. We report clinical outcome information on patients with predominant plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed treatments and outcomes in patients with predominant plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma seen at our institution from 1990 through 2010. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to calculate overall and progression-free survival.
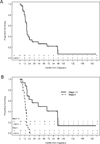
Results: We identified 31 patients with a median age of 63.5 years, of whom 83.3% were male. TNM stage was cT1N0 in 4 patients, cT2N0 in 7, cT3b-4aN0 in 5 and cT4b, N+ or M+ in 15. Median overall survival was 17.7 months (stage I-III vs IV 45.8 vs 13.3). Five of the 16 patients with potentially surgically resectable plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma (pT4aN0M0 or less) received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, 10 underwent initial surgery and 1 was treated only with transurethral resection of bladder tumor. Despite pathological down staging in 80% of the patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, relapses were common. There was no survival difference between patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy or initial surgery, although 7 received adjuvant chemotherapy. Surgical up staging with positive margins was also common for surgery alone. The most common site of recurrence was in the peritoneum (19 of 23 patients) with relapses even in those with a pathological complete response at surgery. In patients who presented with metastatic disease and were treated with chemotherapy median survival was 12.6 months.
Conclusions: Plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma is an aggressive subset with overall poor outcomes. Although down staging is seen with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, there are few long-term survivors. There is a strong predilection for recurrence along the peritoneal lining.
Copyright © 2013 American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial disclosures: All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Editorial comment.J Urol. 2013 May;189(5):1660-1. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.11.194. Epub 2013 Feb 16. J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23419938 No abstract available.
References
-
- Montironi R, Lopez-Beltran A. The 2004 WHO classification of bladder tumors: a summary and commentary. International journal of surgical pathology. 2005;13:143–153. - PubMed
-
- Mai KT, Park PC, Yazdi HM, et al. Plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder report of seven new cases. Eur Urol. 2006;50:1111–1114. - PubMed
-
- Keck B, Stoehr R, Wach S, et al. The plasmacytoid carcinoma of the bladder-rare variant of aggressive urothelial carcinoma. Int J Cancer - PubMed
-
- Kohno T, Kitamura M, Akai H, et al. Plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Int J Urol. 2006;13:485–486. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Beltran A, Requena MJ, Montironi R, et al. Plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Hum Pathol. 2009;40:1023–1028. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

