Steroid-induced microRNA let-7 acts as a spatio-temporal code for neuronal cell fate in the developing Drosophila brain
- PMID: 23160410
- PMCID: PMC3545287
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.298
Steroid-induced microRNA let-7 acts as a spatio-temporal code for neuronal cell fate in the developing Drosophila brain
Abstract
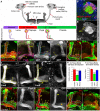
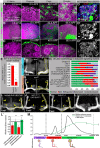
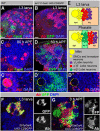
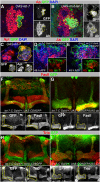
Mammalian neuronal stem cells produce multiple neuron types in the course of an individual's development. Similarly, neuronal progenitors in the Drosophila brain generate different types of closely related neurons that are born at specific time points during development. We found that in the post-embryonic Drosophila brain, steroid hormones act as temporal cues that specify the cell fate of mushroom body (MB) neuroblast progeny. Chronological regulation of neurogenesis is subsequently mediated by the microRNA (miRNA) let-7, absence of which causes learning impairment due to morphological MB defects. The miRNA let-7 is required to regulate the timing of α'/β' to α/β neuronal identity transition by targeting the transcription factor Abrupt. At a cellular level, the ecdysone-let-7-Ab signalling pathway controls the expression levels of the cell adhesion molecule Fasciclin II in developing neurons that ultimately influences their differentiation. Our data propose a novel role for miRNAs as transducers between chronologically regulated developmental signalling and physical cell adhesion.
Figures
Comment in
-
Steroids as external temporal codes act via microRNAs and cooperate with cytokines in differential neurogenesis.Fly (Austin). 2013 Jul-Sep;7(3):173-83. doi: 10.4161/fly.25241. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Fly (Austin). 2013. PMID: 23839338 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Steroids as external temporal codes act via microRNAs and cooperate with cytokines in differential neurogenesis.Fly (Austin). 2013 Jul-Sep;7(3):173-83. doi: 10.4161/fly.25241. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Fly (Austin). 2013. PMID: 23839338 Free PMC article.
-
Steroid Hormone Ecdysone Signaling Specifies Mushroom Body Neuron Sequential Fate via Chinmo.Curr Biol. 2017 Oct 9;27(19):3017-3024.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.08.037. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Curr Biol. 2017. PMID: 28966087
-
Modulators of hormonal response regulate temporal fate specification in the Drosophila brain.PLoS Genet. 2019 Dec 6;15(12):e1008491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008491. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31809495 Free PMC article.
-
Playing Well with Others: Extrinsic Cues Regulate Neural Progenitor Temporal Identity to Generate Neuronal Diversity.Trends Genet. 2017 Dec;33(12):933-942. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2017.08.005. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Trends Genet. 2017. PMID: 28899597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steroid hormones, dietary nutrients, and temporal progression of neurogenesis.Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2021 Feb;43:70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2020.10.008. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2021. PMID: 33127508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The making of the Drosophila mushroom body.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 13;14:1091248. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1091248. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36711013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Noncoding RNA lncR17454 Regulates Metamorphosis of Silkworm Through let-7 miRNA Cluster.J Insect Sci. 2022 May 1;22(3):12. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/ieac028. J Insect Sci. 2022. PMID: 35640247 Free PMC article.
-
General hallmarks of microRNAs in brain evolution and development.RNA Biol. 2015;12(7):701-8. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1048954. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26000728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mamo decodes hierarchical temporal gradients into terminal neuronal fate.Elife. 2019 Sep 23;8:e48056. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48056. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31545163 Free PMC article.
-
Abrupt-mediated control of ninjurins regulates Drosophila sessile haemocyte compartments.Development. 2024 Dec 1;151(23):dev202977. doi: 10.1242/dev.202977. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Development. 2024. PMID: 39545919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahante JE, Daul AL, Li M, Volk ML, Tennessen JM, Miller EA, Rougvie AE (2003) The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs. Dev Cell 4: 625–637 - PubMed
-
- Bashirullah A, Pasquinelli AE, Kiger AA, Perrimon N, Ruvkun G, Thummel CS (2003) Coordinate regulation of small temporal RNAs at the onset of Drosophila metamorphosis. Dev Biol 259: 1–8 - PubMed
-
- Bauer S, Kerr BJ, Patterson PH (2007) The neuropoietic cytokine family in development, plasticity, disease and injury. Nat Rev Neurosci 8: 221–232 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

