HNF1β is essential for nephron segmentation during nephrogenesis
- PMID: 23160512
- PMCID: PMC3537220
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012070756
HNF1β is essential for nephron segmentation during nephrogenesis
Abstract
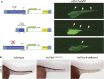
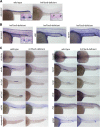
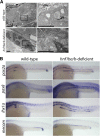
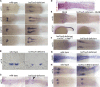
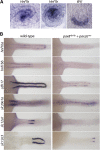
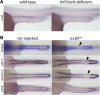
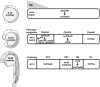
Nephrons comprise a blood filter and an epithelial tubule that is subdivided into proximal and distal segments, but what directs this patterning during kidney organogenesis is not well understood. Using zebrafish, we found that the HNF1β paralogues hnf1ba and hnf1bb, which encode homeodomain transcription factors, are essential for normal segmentation of nephrons. Embryos deficient in hnf1ba and hnf1bb did not express proximal and distal segment markers, yet still developed an epithelial tubule. Initiating hnf1ba/b expression required Pax2a and Pax8, but hnf1ba/b-deficient embryos did not exhibit the expected downregulation of pax2a and pax8 at later stages of development, suggesting complex regulatory loops involving these molecules. Embryos deficient in hnf1ba/b also did not express the irx3b transcription factor, which is responsible for differentiation of the first distal tubule segment. Reciprocally, embryos deficient in irx3b exhibited downregulation of hnf1ba/b transcripts in the distal early segment, suggesting a segment-specific regulatory circuit. Deficiency of hnf1ba/b also led to ectopic expansion of podocytes into the proximal tubule domain. Epistasis experiments showed that the formation of podocytes required wt1a, which encodes the Wilms' tumor suppressor-1 transcription factor, and rbpj, which encodes a mediator of canonical Notch signaling, downstream or parallel to hnf1ba/b. Taken together, these results suggest that Hnf1β factors are essential for normal segmentation of nephrons during kidney organogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Wingert RA, Davidson AJ: The zebrafish pronephros: A model to study nephron segmentation. Kidney Int 73: 1120–1127, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Dawid IB, Breen JJ, Toyama R: LIM domains: Multiple roles as adapters and functional modifiers in protein interactions. Trends Genet 14: 156–162, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Pfeffer PL, Gerster T, Lun K, Brand M, Busslinger M: Characterization of three novel members of the zebrafish Pax2/5/8 family: Dependency of Pax5 and Pax8 expression on the Pax2.1 (noi) function. Development 125: 3063–3074, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Toyama R, Kobayashi M, Tomita T, Dawid IB: Expression of LIM-domain binding protein (ldb) genes during zebrafish embryogenesis. Mech Dev 71: 197–200, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

