Deleting the TGF-β receptor attenuates acute proximal tubule injury
- PMID: 23160515
- PMCID: PMC3507360
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012020139
Deleting the TGF-β receptor attenuates acute proximal tubule injury
Abstract
TGF-β is a profibrotic growth factor in CKD, but its role in modulating the kidney's response to AKI is not well understood. The proximal tubule epithelial cell, which is the main cellular target of AKI, expresses high levels of both TGF-β and its receptors. To determine how TGF-β signaling in this tubular segment affects the response to AKI, we selectively deleted the TGF-β type II receptor in the proximal tubules of mice. This deletion attenuated renal impairment and reduced tubular apoptosis in mercuric chloride-induced injury. In vitro, deficiency of the TGF-β type II receptor protected proximal tubule epithelial cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis, which was mediated in part by Smad-dependent signaling. Taken together, these results suggest that TGF-β signaling in the proximal tubule has a detrimental effect on the response to AKI as a result of its proapoptotic effects.
Figures
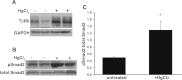

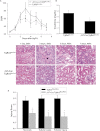
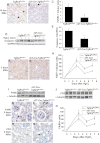
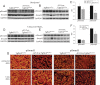


Similar articles
-
Blocking TGF-β and β-Catenin Epithelial Crosstalk Exacerbates CKD.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Dec;28(12):3490-3503. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016121351. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28701516 Free PMC article.
-
Deleting the TGF-β receptor in proximal tubules impairs HGF signaling.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Mar 15;310(6):F499-510. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00446.2015. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26739889 Free PMC article.
-
TNIK depletion induces inflammation and apoptosis in injured renal proximal tubule epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 May 1;326(5):F827-F838. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00262.2023. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38482555 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming Growth Factor-β in the Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease Transition.Nephron. 2019;143(3):154-157. doi: 10.1159/000500093. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Nephron. 2019. PMID: 31039574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming growth factor-β signalling: role and consequences of Smad linker region phosphorylation.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):2017-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770288 Review.
Cited by
-
Epithelial cell TGFβ signaling induces acute tubular injury and interstitial inflammation.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Apr;24(5):787-99. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012101024. Epub 2013 Mar 28. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23539761 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking cell cycle progression through CDK4/6 protects against chronic kidney disease.JCI Insight. 2022 Jun 22;7(12):e158754. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.158754. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35730565 Free PMC article.
-
PHF14: an innate inhibitor against the progression of renal fibrosis following folic acid-induced kidney injury.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 3;7:39888. doi: 10.1038/srep39888. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28045076 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal tubule LPA1 and LPA2 receptors use divergent signaling pathways to additively increase profibrotic cytokine secretion.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021 Mar 1;320(3):F359-F374. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00494.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33427061 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Transforming Growth Factor-β Improves Primary Renal Tubule Cell Differentiation in Long-Term Culture.Tissue Eng Part A. 2023 Feb;29(3-4):102-111. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2022.0147. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Tissue Eng Part A. 2023. PMID: 36274231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coimbra TM, Cieslinski DA, Humes HD: Epidermal growth factor accelerates renal repair in mercuric chloride nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol 259: F438–F443, 1990 - PubMed
-
- Miller SB, Martin DR, Kissane J, Hammerman MR: Hepatocyte growth factor accelerates recovery from acute ischemic renal injury in rats. Am J Physiol 266: F129–F134, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Wrana JL, Attisano L, Cárcamo J, Zentella A, Doody J, Laiho M, Wang XF, Massagué J: TGF beta signals through a heteromeric protein kinase receptor complex. Cell 71: 1003–1014, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK51265/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK062794/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK065123/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK069221/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- L40 DK069221/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083187/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK65123/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075594/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK083187/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK051265/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK075594/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062794/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK79341-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

