Local autoantigen expression as essential gatekeeper of memory T-cell recruitment to islet grafts in diabetic hosts
- PMID: 23160528
- PMCID: PMC3581210
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-0600
Local autoantigen expression as essential gatekeeper of memory T-cell recruitment to islet grafts in diabetic hosts
Abstract
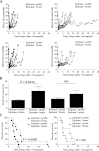
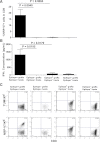
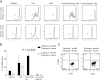
It is generally believed that inflammatory cues can attract noncognate, "bystander" T-cell specificities to sites of inflammation. We have shown that recruitment of naive and in vitro activated autoreactive CD8⁺ T cells into endogenous islets requires local autoantigen expression. Here, we demonstrate that absence of an autoantigen in syngeneic extrapancreatic islet grafts in diabetic hosts renders the grafts "invisible" to cognate memory (and naive) T cells. We monitored the recruitment of islet-specific glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit-related protein (IGRP)₂₀₆₋₂₁₄-reactive CD8⁺ T cells into IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄-competent and IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄-deficient islet grafts in diabetic wild-type or IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄(-/-) nonobese diabetic hosts (harboring either naive and memory T cells or only naive IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄-specific T-cells, respectively). All four host-donor combinations had development of recurrent diabetes within 2 weeks. Wild-type hosts recruited IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄-specific T cells into IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄(+/+) but not IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄(-/-) grafts. In IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄(-/-) hosts, there was no recruitment of IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄-specific T cells, regardless of donor type. Graft-derived IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄ activated naive IGRP₂₀₆₋₂₁₄-specific T cells, but graft destruction invariably predated their recruitment. These results indicate that recurrent diabetes is exclusively driven by autoreactive T cells primed during the primary autoimmune response, and demonstrate that local antigen expression is a sine qua non requirement for accumulation of memory T cells into islet grafts. These findings underscore the importance of tackling autoreactive T-cell memory after β-cell replacement therapy.
Figures

References
-
- DiLorenzo T, Graser T, Ono T, et al. Major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted T cells are required for all but end stages of diabetes development in nonobese diabetic mice and use a prevalent T cell receptor alpha chain gene rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998;95:12538–12543 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verdaguer J, Yoon JW, Anderson B, et al. Acceleration of spontaneous diabetes in TCR-beta-transgenic nonobese diabetic mice by beta-cell cytotoxic CD8+ T cells expressing identical endogenous TCR-alpha chains. J Immunol 1996;157:4726–4735 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

