Orbitofrontal sulcogyral patterns are related to temperamental risk for psychopathology
- PMID: 23160816
- PMCID: PMC3907929
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nss126
Orbitofrontal sulcogyral patterns are related to temperamental risk for psychopathology
Abstract
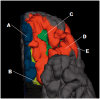
There are marked individual differences in the pattern of cortical (sulcogyral) folding in the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC), and there is a growing literature suggesting that these individual differences are associated with risk for psychotic disorders. To date, however, no study has investigated whether OFC folding patterns are associated with broader risk factors relevant to a range of psychopathology. This study helps address this knowledge gap by examining whether OFC sulcogyral folding patterns are associated with putative risk factors, specifically affective temperament and psychiatric symptoms, in a large community sample (N = 152) of adolescents. Results showed that the most common pattern of folding ('Type I', marked by discontinuity of the medial orbital sulcus and continuity of the lateral orbital sulcus) was associated with low levels of Surgency, high levels of Negative Affectivity (in girls) and higher depressive symptoms. This pattern was also associated with reduced thickness of OFC gray matter. Overall, the findings, combined with previous work, suggest some specificity of neurodevelopmental risk for different types of psychopathology. Thus, these results have the potential to inform the early identification of at-risk individuals.
Keywords: adolescence; gyrification; orbitofrontal cortex; risk; temperament.
Figures

References
-
- Achenbach TM. Manual for the Youth Self-report and 1991 Profiles. Burlington, VT: Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont; 1991.
-
- Bartley AJ, Jones DW, Weinberger DR. Genetic variability of human brain size and cortical gyral patterns. Brain. 1997;120:257–69. - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Brown G, Epstein N, Steer RA. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety - psychometric properties. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1988;56(6):893–7. - PubMed
-
- Berlin HA, Rolls ET, Kischka U. Impulsivity, time perception, emotion and reinforcement sensitivity in patients with orbitofrontal cortex lesions. Brain. 2004;127(5):1108–26. - PubMed
-
- Bremner JD, Vythilingam M, Nazeer A, et al. Reduced volume of orbitofrontal cortex in major depression. Biological Psychiatry. 2002;51:273–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

