Inhibition of the proliferation of acquired aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast cancer cells by histone deacetylase inhibitor LBH589 (panobinostat)
- PMID: 23160924
- PMCID: PMC3637924
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-012-2332-x
Inhibition of the proliferation of acquired aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast cancer cells by histone deacetylase inhibitor LBH589 (panobinostat)
Abstract
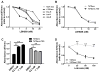
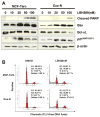
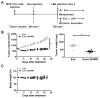
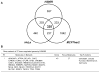
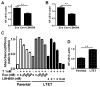
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are important drugs for treating postmenopausal patients with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. However, acquired resistance to AI therapies is a significant problem. Our study has revealed that the histone deacetylase inhibitor LBH589 treatment abrogated growth of AI-resistant cells in vitro and in vivo, causing cell cycle G2/M arrest and induced apoptosis. LBH589 treatment also reduced the level of NF-κB1 which is overexpressed when AI resistance develops. Analyzing paired tumor specimens from 12 patients, we found that NF-κB1 expression was increased in recurrent AI-resistant tumors as compared to the paired primary tumors before AI treatment. This finding was consistent with up-regulated NF-κB1 expression seen in a collection of well-established AI-resistant cell lines. Furthermore, knockdown of NF-κB1 expression significantly suppressed the proliferation of AI-resistant cells. Treatment of AI-resistant cell lines with LBH589 suppressed NF-κB1 mRNA and protein expression. In addition, LBH589 treatment abrogated growth of AI-resistant tumors in mice, and was associated with significantly decreased levels of NF-κB1 in tumors. In all, our findings strongly support further investigation of LBH589 as a novel therapeutic strategy for patients with AI-resistant breast cancer, in part by suppressing the NF-κB1 pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


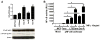
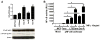
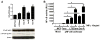
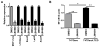
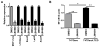


Similar articles
-
The HDAC inhibitor LBH589 (panobinostat) is an inhibitory modulator of aromatase gene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 15;107(24):11032-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000917107. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534486 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589) on the growth of ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2016 Sep 15;9(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13048-016-0267-2. J Ovarian Res. 2016. PMID: 27633667 Free PMC article.
-
The antimelanoma activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589) is mediated by direct tumor cytotoxicity and increased tumor immunogenicity.Melanoma Res. 2013 Oct;23(5):341-8. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0b013e328364c0ed. Melanoma Res. 2013. PMID: 23963286 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting triple-negative breast cancer cells with the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 May 21;14(3):R79. doi: 10.1186/bcr3192. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22613095 Free PMC article.
-
Profile of panobinostat and its potential for treatment in solid tumors: an update.Onco Targets Ther. 2013 Nov 15;6:1613-24. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S30773. eCollection 2013. Onco Targets Ther. 2013. PMID: 24265556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-canonical NF-κB pathway activation predicts outcome in borderline oestrogen receptor positive breast carcinoma.Br J Cancer. 2016 Jul 26;115(3):322-31. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.204. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Br J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27404455 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Strategy to Co-target Estrogen Receptor and Nuclear Factor κB Pathways with Hybrid Drugs for Breast Cancer Therapy.Horm Cancer. 2017 Jun;8(3):135-142. doi: 10.1007/s12672-017-0294-5. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Horm Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28396978 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Therapeutic Combination Targets the Growth of Letrozole-Resistant Breast Cancer through Decreased Cyclin B1.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 28;15(7):1632. doi: 10.3390/nu15071632. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049472 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting breast cancer stem cells in triple-negative breast cancer using a combination of LBH589 and salinomycin.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Jun;151(2):281-94. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3376-5. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 25904215 Free PMC article.
-
Aromatase Acetylation Patterns and Altered Activity in Response to Sirtuin Inhibition.Mol Cancer Res. 2018 Oct;16(10):1530-1542. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0047. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Mol Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29921733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Josefsson ML, Leinster SJ. Aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen as adjuvant hormonal therapy for oestrogen sensitive early breast cancer in post-menopausal women: meta-analyses of monotherapy, sequenced therapy and extended therapy. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland) 2010;19 (2):76–83. - PubMed
-
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Baum M, Buzdar A, Howell A, Dowsett M, Forbes JF. Effect of anastrozole and tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for early-stage breast cancer: 10-year analysis of the ATAC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11 (12):1135–1141. - PubMed
-
- van de Velde CJ, Rea D, Seynaeve C, Putter H, Hasenburg A, Vannetzel JM, Paridaens R, Markopoulos C, Hozumi Y, Hille ET, Kieback DG, Asmar L, Smeets J, Nortier JW, Hadji P, Bartlett JM, Jones SE. Adjuvant tamoxifen and exemestane in early breast cancer (TEAM): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;377 (9762):321–331. - PubMed
-
- Regan MM, Neven P, Giobbie-Hurder A, Goldhirsch A, Ejlertsen B, Mauriac L, Forbes JF, Smith I, Lang I, Wardley A, Rabaglio M, Price KN, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thurlimann B. Assessment of letrozole and tamoxifen alone and in sequence for postmenopausal women with steroid hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: the BIG 1–98 randomised clinical trial at 8.1 years median follow-up. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12 (12):1101–1108. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

