Chlorobaculum tepidum TLS displays a complex transcriptional response to sulfide addition
- PMID: 23161024
- PMCID: PMC3553837
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01342-12
Chlorobaculum tepidum TLS displays a complex transcriptional response to sulfide addition
Abstract
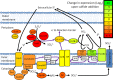
Chlorobaculum tepidum is a green sulfur bacterium (GSB) that is a model system for phototrophic sulfur oxidation. Despite over 2 decades of research, conspicuous gaps exist in our understanding of its electron donor metabolism and regulation. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was used to provide a global picture of the C. tepidum transcriptome during growth on thiosulfate as the sole electron donor and at time points following the addition of sulfide to such a culture. Following sulfide addition, 121 to 150 protein-coding genes displayed significant changes in expression depending upon the time point. These changes included a rapid decrease in expression of thiosulfate and elemental sulfur oxidation genes. Genes and gene loci with increased expression included CT1087, encoding a sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase required for growth in high sulfide concentrations; a polysulfide reductase-like complex operon, psrABC (CT0496 to CT0494); and, surprisingly, a large cluster of genes involved in iron acquisition. Finally, two genes that are conserved as a cassette in anaerobic bacteria and archaea, CT1276 and CT1277, displayed a strong increase in expression. The CT1277 gene product contains a DNA-binding domain, suggesting a role for it in sulfide-dependent gene expression changes.
Figures

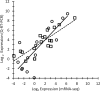
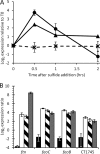
 , dashed line; mean ± SD of 59 genes). (B) qRT-PCR expression analysis of RNA harvested from cultures grown on thiosulfate (black) or 30 min after addition of sulfide to 2 mM (white) or 6 mM (stripes) and trace metal limitation (gray). Expression is reported as log2 of the expression ratio relative to sigA, and values are means ± SDs among all technical replicates (n ≥ 5).
, dashed line; mean ± SD of 59 genes). (B) qRT-PCR expression analysis of RNA harvested from cultures grown on thiosulfate (black) or 30 min after addition of sulfide to 2 mM (white) or 6 mM (stripes) and trace metal limitation (gray). Expression is reported as log2 of the expression ratio relative to sigA, and values are means ± SDs among all technical replicates (n ≥ 5).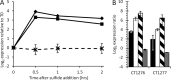
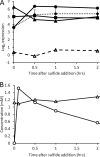
 , dashed line) measured by RNA-seq following the addition of sulfide. (B) qRT-PCR expression analysis of RNA harvested from cultures grown on thiosulfate (black) or 30 min after addition of sulfide to 2 mM (white) or 6 mM (stripes) and trace metal limitation (gray). Expression ratios are relative to sigA and are means ± SDs among all technical replicates (n ≥ 5).
, dashed line) measured by RNA-seq following the addition of sulfide. (B) qRT-PCR expression analysis of RNA harvested from cultures grown on thiosulfate (black) or 30 min after addition of sulfide to 2 mM (white) or 6 mM (stripes) and trace metal limitation (gray). Expression ratios are relative to sigA and are means ± SDs among all technical replicates (n ≥ 5).
References
-
- Jørgensen BB, Fossing Wirsen CO, Jannasch HW. 1991. Sulfide oxidation in the anoxic Black Sea chemocline. Deep Sea Res. A 38:S1083–S1103 doi:. - DOI
-
- Petri R, Imhoff J. 2001. Genetic analysis of sea-ice bacterial communities of the Western Baltic Sea using an improved double gradient method. Polar Biol. 24:252–257 doi:. - DOI
-
- Wahlund TM, Woese CR, Castenholz RW, Madigan MT. 1991. A thermophilic green sulfur bacterium from New Zealand hot springs, Chlorobium tepidum sp. nov. Arch. Microbiol. 156:81–90 doi:. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

