Domain analysis of ArcS, the hybrid sensor kinase of the Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 Arc two-component system, reveals functional differentiation of its two receiver domains
- PMID: 23161031
- PMCID: PMC3554005
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01715-12
Domain analysis of ArcS, the hybrid sensor kinase of the Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 Arc two-component system, reveals functional differentiation of its two receiver domains
Abstract
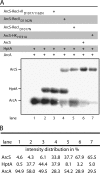
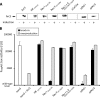
In all species of the genus Shewanella, the redox-sensing Arc two-component system consists of the response regulator ArcA, the sensor kinase ArcS, and the separate phosphotransfer protein HptA. Compared to its counterpart ArcB in Escherichia coli, ArcS has a significantly different domain structure. Resequencing and reannotation revealed that in the N-terminal part, ArcS possesses a periplasmic CaChe-sensing domain bracketed by two transmembrane domains and, moreover, that ArcS has two cytoplasmic PAS-sensing domains and two receiver domains, compared to a single one of each in ArcB. Here, we used a combination of in vitro phosphotransfer studies on purified proteins and phenotypic in vivo mutant analysis to determine the roles of the different domains in ArcS function. The analysis revealed that phosphotransfer occurs from and toward the response regulator ArcA and involves mainly the C-terminal RecII domain. However, RecI also can receive a phosphate from HptA. In addition, the PAS-II domain, located upstream of the histidine kinase domain, is crucial for function. The results support a model in which phosphorylation of RecI stimulates histidine kinase activity of ArcS in order to maintain an appropriate level of phosphorylated ArcA according to environmental conditions. In addition, the study reveals some fundamental mechanistic differences between ArcS/HptA and ArcB with respect to signal perception and phosphotransfer despite functional conservation of the Arc system in Shewanella and E. coli.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ArcS, the cognate sensor kinase in an atypical Arc system of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 May;76(10):3263-74. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00512-10. Epub 2010 Mar 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20348304 Free PMC article.
-
Anaerobic regulation by an atypical Arc system in Shewanella oneidensis.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Jun;56(5):1347-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04628.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15882425
-
A dual-signaling mechanism mediated by the ArcB hybrid sensor kinase containing the histidine-containing phosphotransfer domain in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1998 Aug;180(15):3973-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.15.3973-3977.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9683496 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and molecular physiology of Escherichia coli in the adaptation to aerobic environments.J Biochem. 1996 Dec;120(6):1055-63. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021519. J Biochem. 1996. PMID: 9010748 Review.
-
The ArcAB Two-Component System: Function in Metabolism, Redox Control, and Infection.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2022 Jun 15;86(2):e0011021. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00110-21. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35442087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Shewanella oneidensis arcA Mutation Impairs Aerobic Growth Mainly by Compromising Translation.Life (Basel). 2021 Sep 6;11(9):926. doi: 10.3390/life11090926. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34575075 Free PMC article.
-
The mxd operon in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 is induced in response to starvation and regulated by ArcS/ArcA and BarA/UvrY.BMC Microbiol. 2013 May 27;13:119. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-119. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23705927 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic characterization of rare earth binding by Shewanella oneidensis.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 25;13(1):15975. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42742-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37749198 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide Transport System Links Physiological Roles of σE and ArcA in the Cell Envelope Biogenesis in Shewanella oneidensis.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0069021. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00690-21. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34406804 Free PMC article.
-
Diversification of signal identity and modus operandi of the Haemophilus influenzae PAS-less ArcB sensor kinase.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 5;19(12):e0315238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315238. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39637204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stock AM, Robinson VL, Goudreau PN. 2000. Two-component signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69:183–215 - PubMed
-
- Forst SA, Roberts DL. 1994. Signal transduction by the EnvZ-OmpR phosphotransfer system in bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 145:363–373 - PubMed
-
- Salmon KA, Hung SP, Steffen NR, Krupp R, Baldi P, Hatfield GW, Gunsalus RP. 2005. Global gene expression profiling in Escherichia coli K12: effects of oxygen availability and ArcA. J. Biol. Chem. 280:15084–15096 - PubMed
-
- Egger LA, Park H, Inouye M. 1997. Signal transduction via the histidyl-aspartyl phosphorelay. Genes Cells 2:167–184 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

