Identification and characterization of a high-affinity choline uptake system of Brucella abortus
- PMID: 23161032
- PMCID: PMC3554019
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01929-12
Identification and characterization of a high-affinity choline uptake system of Brucella abortus
Abstract
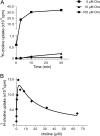
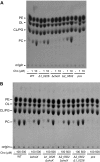
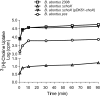
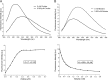
Phosphatidylcholine (PC), a common phospholipid of the eukaryotic cell membrane, is present in the cell envelope of the intracellular pathogen Brucella abortus, the etiological agent of bovine brucellosis. In this pathogen, the biosynthesis of PC proceeds mainly through the phosphatidylcholine synthase pathway; hence, it relies on the presence of choline in the milieu. These observations imply that B. abortus encodes an as-yet-unknown choline uptake system. Taking advantage of the requirement of choline uptake for PC synthesis, we devised a method that allowed us to identify a homologue of ChoX, the high-affinity periplasmic binding protein of the ABC transporter ChoXWV. Disruption of the choX gene completely abrogated PC synthesis at low choline concentrations in the medium, thus indicating that it is a high-affinity transporter needed for PC synthesis via the PC synthase (PCS) pathway. However, the synthesis of PC was restored when the mutant was incubated in media with higher choline concentrations, suggesting the presence of an alternative low-affinity choline uptake activity. By means of a fluorescence-based equilibrium-binding assay and using the kinetics of radiolabeled choline uptake, we show that ChoX binds choline with an extremely high affinity, and we also demonstrate that its activity is inhibited by increasing choline concentrations. Cell infection assays indicate that ChoX activity is required during the first phase of B. abortus intracellular traffic, suggesting that choline concentrations in the early and intermediate Brucella-containing vacuoles are limited. Altogether, these results suggest that choline transport and PC synthesis are strictly regulated in B. abortus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brucella abortus synthesizes phosphatidylcholine from choline provided by the host.J Bacteriol. 2006 Mar;188(5):1929-34. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.5.1929-1934.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16484204 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylethanolamine synthesis is required for optimal virulence of Brucella abortus.J Bacteriol. 2008 Dec;190(24):8197-203. doi: 10.1128/JB.01069-08. Epub 2008 Oct 17. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18931122 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a Brucella abortus ATP-binding cassette transporter homolog to Rhizobium meliloti ExsA and its role in virulence and protection in mice.Infect Immun. 2002 Sep;70(9):5036-44. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.9.5036-5044.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12183550 Free PMC article.
-
The Sinorhizobium meliloti ABC transporter Cho is highly specific for choline and expressed in bacteroids from Medicago sativa nodules.J Bacteriol. 2004 Sep;186(18):5988-96. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.18.5988-5996.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15342567 Free PMC article.
-
Brucellosis vaccines based on the open reading frames from genomic island 3 of Brucella abortus.Vaccine. 2018 May 17;36(21):2928-2936. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.04.014. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 29685597 Review.
Cited by
-
ChoK-ing the Pathogenic Bacteria: Potential of Human Choline Kinase Inhibitors as Antimicrobial Agents.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jul 9;2020:1823485. doi: 10.1155/2020/1823485. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32695809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering the Hidden Credentials of Brucella Virulence.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2021 Feb 10;85(1):e00021-19. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00021-19. Print 2021 Feb 17. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33568459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Phospholipid N-Methyltransferase and Phosphatidylcholine Synthase Pathways and the ChoXWV Choline Uptake System Involved in Phosphatidylcholine Synthesis Are Widely Conserved in Most, but Not All Brucella Species.Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 4;12:614243. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.614243. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34421831 Free PMC article.
-
Brucellosis: Bacteriology, pathogenesis, epidemiology and role of the metallophores in virulence: a review.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jul 8;15:1621230. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1621230. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40697821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Brucella Cell Envelope.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2023 Sep 15;77:233-253. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-032521-013159. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37104660 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blusztajn JK. 1998. Choline, a vital amine. Science 281: 794–795 - PubMed
-
- Michel V, Yuan Z, Ramsubir S, Bakovic M. 2006. Choline transport for phospholipid synthesis. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 231: 490–504 - PubMed
-
- Zeisel SH, Da Costa KA, Franklin PD, Alexander EA, Lamont JT, Sheard NF, Beiser A. 1991. Choline, an essential nutrient for humans. FASEB J. 5: 2093–2098 - PubMed
-
- Zeisel SH. 1997. Choline: essential for brain development and function. Adv. Pediatr. 44: 263–295 - PubMed
-
- Aktas M, Wessel M, Hacker S, Klusener S, Gleichenhagen J, Narberhaus F. 2010. Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and its significance in bacteria interacting with eukaryotic cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 89: 888–894 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

