Correlates of retention in HIV care after release from jail: results from a multi-site study
- PMID: 23161210
- PMCID: PMC3714328
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-012-0372-1
Correlates of retention in HIV care after release from jail: results from a multi-site study
Abstract
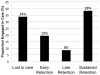
Retention in care is key to effective HIV treatment, but half of PLWHA in the US are continuously engaged in care. Incarcerated individuals are an especially challenging population to retain, and empiric data specific to jail detainees is lacking. We prospectively evaluated correlates of retention in care for 867 HIV-infected jail detainees enrolled in a 10-site demonstration project. Sustained retention in care was defined as having a clinic visit during each quarter in the 6 month post-release period. The following were independently associated with retention: being male (AOR = 2.10, p ≤ 0.01), heroin use (AOR 1.49, p = 0.04), having an HIV provider (AOR 1.67, p = 0.02), and receipt of services: discharge planning (AOR 1.50, p = 0.02) and disease management session (AOR 2.25, p ≤ 0.01) during incarceration; needs assessment (AOR 1.59, p = 0.02), HIV education (AOR 2.03, p ≤ 0.01), and transportation assistance (AOR 1.54, p = 0.02) after release. Provision of education and case management services improve retention in HIV care after release from jail.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Advancing HIV Prevention Initiative. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2005.
-
- Lima VD, Johnston K, Hogg RS, Levy AR, Harrigan PR, Anema A, et al. Expanded access to highly active antiretroviral therapy: a potentially powerful strategy to curb the growth of the HIV epidemic. J Infect Dis. 2008 Jul 1;198(1):59–67. - PubMed
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. Getting to Zero. 2010.
-
- Marks G, Gardner LI, Craw J, Crepaz N. Entry and retention in medical care among HIV-diagnosed persons: a meta-analysis. AIDS. 2010 Nov;24(17):2665–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

