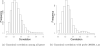Incorporating network structure in integrative analysis of cancer prognosis data
- PMID: 23161517
- PMCID: PMC3909475
- DOI: 10.1002/gepi.21697
Incorporating network structure in integrative analysis of cancer prognosis data
Abstract
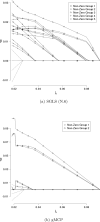
In high-throughput cancer genomic studies, markers identified from the analysis of single datasets may have unsatisfactory properties because of low sample sizes. Integrative analysis pools and analyzes raw data from multiple studies, and can effectively increase sample size and lead to improved marker identification results. In this study, we consider the integrative analysis of multiple high-throughput cancer prognosis studies. In the existing integrative analysis studies, the interplay among genes, which can be described using the network structure, has not been effectively accounted for. In network analysis, tightly connected nodes (genes) are more likely to have related biological functions and similar regression coefficients. The goal of this study is to develop an analysis approach that can incorporate the gene network structure in integrative analysis. To this end, we adopt an AFT (accelerated failure time) model to describe survival. A weighted least squares approach, which has low computational cost, is adopted for estimation. For marker selection, we propose a new penalization approach. The proposed penalty is composed of two parts. The first part is a group MCP penalty, and conducts gene selection. The second part is a Laplacian penalty, and smoothes the differences of coefficients for tightly connected genes. A group coordinate descent approach is developed to compute the proposed estimate. Simulation study shows satisfactory performance of the proposed approach when there exist moderate-to-strong correlations among genes. We analyze three lung cancer prognosis datasets, and demonstrate that incorporating the network structure can lead to the identification of important genes and improved prediction performance.
© 2012 WILEY PERIODICALS, INC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrative analysis of high-throughput cancer studies with contrasted penalization.Genet Epidemiol. 2014 Feb;38(2):144-51. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21781. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Genet Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 24395534 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of Cancer Diagnosis Studies with Composite Penalization.Scand Stat Theory Appl. 2014 Mar 1;41(1):87-103. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9469.2012.00816.x. Scand Stat Theory Appl. 2014. PMID: 24578589 Free PMC article.
-
Sparse group penalized integrative analysis of multiple cancer prognosis datasets.Genet Res (Camb). 2013 Jun;95(2-3):68-77. doi: 10.1017/S0016672313000086. Genet Res (Camb). 2013. PMID: 23938111 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting Similarity of Sparsity Structures in Integrative Analysis with Penalization.J Am Stat Assoc. 2017;112(517):342-350. doi: 10.1080/01621459.2016.1139497. Epub 2017 May 3. J Am Stat Assoc. 2017. PMID: 30100648 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding genomic alterations in cancer genomes using an integrative network approach.Cancer Lett. 2013 Nov 1;340(2):261-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.11.050. Epub 2012 Dec 22. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23266571 Review.
Cited by
-
Ensemble-based network aggregation improves the accuracy of gene network reconstruction.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 12;9(11):e106319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106319. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25390635 Free PMC article.
-
GRIA: Graphical Regularization for Integrative Analysis.Proc SIAM Int Conf Data Min. 2020;2020:604-612. doi: 10.1137/1.9781611976236.68. Proc SIAM Int Conf Data Min. 2020. PMID: 32440369 Free PMC article.
-
Structured Analysis of the High-dimensional FMR Model.Comput Stat Data Anal. 2020 Apr;144:106883. doi: 10.1016/j.csda.2019.106883. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Comput Stat Data Anal. 2020. PMID: 32863493 Free PMC article.
-
Robust network-based analysis of the associations between (epi)genetic measurements.J Multivar Anal. 2018 Nov;168:119-130. doi: 10.1016/j.jmva.2018.06.009. Epub 2018 Jul 10. J Multivar Anal. 2018. PMID: 30983643 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative sparse principal component analysis of gene expression data.Genet Epidemiol. 2017 Dec;41(8):844-865. doi: 10.1002/gepi.22089. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Genet Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 29114920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agathanggelou A, Bieche I, Ahmed-Choudhury J, Nicke B, Dammann R, Baksh S, Gao B, Minna JD, Downward J, Maher ER, Latif F. Identification of novel gene expression targets for the ras association domain family 1 (rassf1a) tumor suppressor gene in non-small cell lung cancer and neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63(17):5344–5351. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous