SILAC-based quantitative proteomic analysis of gastric cancer secretome
- PMID: 23161554
- PMCID: PMC3804263
- DOI: 10.1002/prca.201200069
SILAC-based quantitative proteomic analysis of gastric cancer secretome
Abstract
Purpose: Gastric cancer is a commonly occurring cancer in Asia and one of the leading causes of cancer deaths. However, there is no reliable blood-based screening test for this cancer. Identifying proteins secreted from tumor cells could lead to the discovery of clinically useful biomarkers for early detection of gastric cancer.
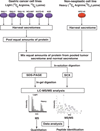
Experimental design: A SILAC-based quantitative proteomic approach was employed to identify secreted proteins that were differentially expressed between neoplastic and non-neoplastic gastric epithelial cells. Proteins from the secretome were subjected to SDS-PAGE and SCX-based fractionation, followed by mass spectrometric analysis on an LTQ-Orbitrap Velos mass spectrometer. Immunohistochemical labeling was employed to validate a subset of candidates using tissue microarrays.
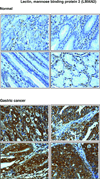
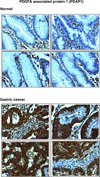
Results: We identified 2205 proteins in the gastric cancer secretome of which 263 proteins were overexpressed greater than fourfold in gastric cancer-derived cell lines as compared to non-neoplastic gastric epithelial cells. Three candidate proteins, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9), lectin mannose binding 2 (LMAN2), and PDGFA-associated protein 1 (PDAP1) were validated by immunohistochemical labeling.
Conclusions and clinical relevance: We report here the largest cancer secretome described to date. The novel biomarkers identified in the current study are excellent candidates for further testing as early detection biomarkers for gastric adenocarcinoma.
© 2013 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures


Similar articles
-
SILAC-based quantitative proteomic approach to identify potential biomarkers from the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma secretome.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Oct 15;10(8):796-810. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.8.12914. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20686364 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis of PCSK9 gain of function in human hepatic HuH7 cells.J Proteome Res. 2011 Apr 1;10(4):2011-26. doi: 10.1021/pr2000072. Epub 2011 Mar 10. J Proteome Res. 2011. PMID: 21332221
-
Posttranslational modification of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 is differentially regulated in response to distinct cardiometabolic treatments as revealed by targeted proteomics.J Clin Lipidol. 2018 Jul-Aug;12(4):1027-1038. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2018.03.092. Epub 2018 Apr 3. J Clin Lipidol. 2018. PMID: 29699916
-
Proprotein convertases subtilisin/kexin type 9, an enzyme turned escort protein: hepatic and extra hepatic functions.J Diabetes. 2013 Dec;5(4):391-405. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12064. Epub 2013 Jul 8. J Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23714205 Review.
-
PCSK9 (Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) inhibitors: past, present, and the future.Eur Heart J. 2015 Sep 21;36(36):2415-24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv174. Epub 2015 May 12. Eur Heart J. 2015. PMID: 25971287 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of PCSK9 as a prognostic and immune-related influencing factor in tumorigenesis: a pan-cancer analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 4;13:1134063. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1134063. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37860186 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9): from bench to bedside.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Jan 8;9(1):13. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01690-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38185721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SEPROGADIC - serum protein-based gastric cancer prediction model for prognosis and selection of proper adjuvant therapy.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 15;8(1):16892. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34858-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30442939 Free PMC article.
-
The evolving landscape of PCSK9 inhibition in cancer.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 15;949:175721. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175721. Epub 2023 Apr 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37059376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insight into the Evolving Role of PCSK9.Metabolites. 2022 Mar 17;12(3):256. doi: 10.3390/metabo12030256. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35323699 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Roth AD. Curative treatment of gastric cancer: towards a multidisciplinary approach? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2003;46:59–100. - PubMed
-
- Ebert MP, Malfertheiner P. Review article: Pathogenesis of sporadic and familial gastric cancer--implications for clinical management and cancer prevention. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:1059–1066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

