Replicative mechanisms of CNV formation preferentially occur as intrachromosomal events: evidence from Potocki-Lupski duplication syndrome
- PMID: 23161748
- PMCID: PMC3554201
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/dds482
Replicative mechanisms of CNV formation preferentially occur as intrachromosomal events: evidence from Potocki-Lupski duplication syndrome
Abstract
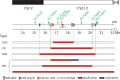
Copy number variations (CNVs) in the human genome contribute significantly to disease. De novo CNV mutations arise via genomic rearrangements, which can occur in 'trans', i.e. via interchromosomal events, or in 'cis', i.e. via intrachromosomal events. However, what molecular mechanisms occur between chromosomes versus between or within chromatids has not been systematically investigated. We hypothesized that distinct CNV mutational mechanisms, based on their intrinsic properties, may occur in a biased intrachromosomal versus interchromosomal manner. Here, we studied 62 genomic duplications observed in association with sporadic Potocki-Lupski syndrome (PTLS), in which multiple mutational mechanisms appear to be operative. Intriguingly, more interchromosomal than intrachromosomal events were identified in recurrent PTLS duplications mediated by non-allelic homologous recombination, whereas the reciprocal distribution was found for replicative mechanisms and non-homologous end-joining, likely reflecting the differences in spacial proximity of homologous chromosomes during different mutational processes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reciprocal deletion and duplication of 17p11.2-11.2: Korean patients with Smith-Magenis syndrome and Potocki-Lupski syndrome.J Korean Med Sci. 2012 Dec;27(12):1586-90. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.12.1586. Epub 2012 Dec 7. J Korean Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 23255863 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of uncommon recurrent Potocki-Lupski syndrome-associated duplications and the distribution of rearrangement types and mechanisms in PTLS.Am J Hum Genet. 2010 Mar 12;86(3):462-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.02.001. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Am J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20188345 Free PMC article.
-
Inherited dup(17)(p11.2p11.2): expanding the phenotype of the Potocki-Lupski syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Feb;164A(2):500-4. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36287. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Am J Med Genet A. 2014. PMID: 24311450 Review.
-
Nonrecurrent 17p11.2p12 Rearrangement Events that Result in Two Concomitant Genomic Disorders: The PMP22-RAI1 Contiguous Gene Duplication Syndrome.Am J Hum Genet. 2015 Nov 5;97(5):691-707. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.10.003. Am J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 26544804 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms for recurrent and complex human genomic rearrangements.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012 Jun;22(3):211-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.02.012. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012. PMID: 22440479 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromosome rearrangements via template switching between diverged repeated sequences.Genes Dev. 2014 Nov 1;28(21):2394-406. doi: 10.1101/gad.250258.114. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 25367035 Free PMC article.
-
Polymerase δ replicates both strands after homologous recombination-dependent fork restart.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Nov;22(11):932-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3100. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26436826 Free PMC article.
-
Pronounced maternal parent-of-origin bias for type-1 NF1 microdeletions.Hum Genet. 2018 May;137(5):365-373. doi: 10.1007/s00439-018-1888-x. Epub 2018 May 5. Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29730711
-
Megabase Length Hypermutation Accompanies Human Structural Variation at 17p11.2.Cell. 2019 Mar 7;176(6):1310-1324.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.045. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Cell. 2019. PMID: 30827684 Free PMC article.
-
CNV instability associated with DNA replication dynamics: evidence for replicative mechanisms in CNV mutagenesis.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Mar 15;24(6):1574-83. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu572. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 25398944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang F., Gu W., Hurles M.E., Lupski J.R. Copy number variation in human health, disease, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2009;10:451–481. doi:10.1146/annurev.genom.9.081307.164217. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lupski J.R., Belmont J.W., Boerwinkle E., Gibbs R.A. Clan genomics and the complex architecture of human disease. Cell. 2011;147:32–43. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lupski J.R. New mutations and intellectual function. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:1036–1038. doi:10.1038/ng1210-1036. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boone P.M., Wiszniewski W., Lupski J.R. Genomic medicine and neurological disease. Hum. Genet. 2011;130:103–121. doi:10.1007/s00439-011-1001-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reik W., Walter J. Genomic imprinting: parental influence on the genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001;2:21–32. doi:10.1038/35047554. - DOI - PubMed

