Motor representations in the intact hemisphere of the rat are reduced after repetitive training of the impaired forelimb
- PMID: 23161864
- PMCID: PMC3962819
- DOI: 10.1177/1545968312465193
Motor representations in the intact hemisphere of the rat are reduced after repetitive training of the impaired forelimb
Abstract
Background: During recovery from a unilateral cortical stroke, spared cortical motor areas in the contralateral (intact) cerebral cortex are recruited. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that compensation with the less-impaired limb may have a detrimental inhibitory effect on the intact cortical hemisphere and could impede recovery of the more-impaired limb. However, evidence from detailed neurophysiological mapping studies in animal models is lacking.
Objectives: The present study examines neurophysiological changes in the intact hemisphere of the rat following a unilateral ischemic infarct to cortical forelimb motor areas.
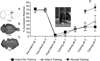
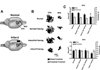
Methods: A total of 8 rats were trained for 2 weeks on a reach and retrieval task prior to an ischemic infarct induced by the vasoconstrictor endothelin-1 injected into the cortical gray matter encompassing the 2 forelimb motor representations: the caudal forelimb area (CFA) and the rostral forelimb area (RFA). Animals were randomly assigned to an infarct/training group (n = 4) or an infarct/no-training group (ie, spontaneous recovery, n = 4). After a 5-week postinfarct period, motor areas of the intact hemisphere (CFA and RFA) were characterized using intracortical microstimulation techniques. The resulting maps of evoked movements were compared with maps derived from CFA and RFA in normal rats (normal, n = 5; normal/training, n = 4).
Results: Compared with the normal/no-training group, CFA representations were significantly smaller in the infarct/training group but not in the infarct/no-training group. No significant differences were found in RFA.
Conclusions: Repetitive training of the more-impaired forelimb during the postinfarct recovery period reduces the size of motor representations in the intact hemisphere.
Figures
References
-
- Adkins DL, Voorhies AC, Jones TA. Behavioral and neuroplastic effects of focal endothelin-1 induced sensorimotor cortex lesions. Neuroscience. 2004;128(3):473–486. - PubMed
-
- Napieralski JA, Butler AK, Chesselet MF. Anatomical and functional evidence for lesion-specific sprouting of corticostriatal input in the adult rat. J Comp Neurol. 1996 Sep 30;373(4):484–497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

