A Rab32-dependent pathway contributes to Salmonella typhi host restriction
- PMID: 23162001
- PMCID: PMC3693731
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1229224
A Rab32-dependent pathway contributes to Salmonella typhi host restriction
Abstract
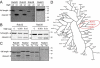
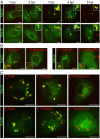
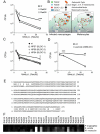
Unlike other Salmonellae, the intracellular bacterial human pathogen Salmonella Typhi exhibits strict host specificity. The molecular bases for this restriction are unknown. Here we found that the expression of a single type III secretion system effector protein from broad-host Salmonella Typhimurium allowed Salmonella Typhi to survive and replicate within macrophages and tissues from mice, a nonpermissive host. This effector proteolytically targeted Rab32, which controls traffic to lysosome-related organelles in conjunction with components of the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelle complexes (BLOCs). RNA interference-mediated depletion of Rab32 or of an essential component of a BLOC complex was sufficient to allow S. Typhi to survive within mouse macrophages. Furthermore, S. Typhi was able to survive in macrophages from mice defective in BLOC components.
Figures
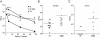
Comment in
-
Bacterial pathogenesis: Salmonella's skeleton key.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Jan;11(1):6. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2938. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23241848 No abstract available.
-
A novel anti-microbial function for a familiar Rab GTPase.Small GTPases. 2013 Oct-Dec;4(4):252-4. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.27282. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Small GTPases. 2013. PMID: 24321888 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohl ME, Miller SI. Salmonella: a model for bacterial pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2001;52:259. - PubMed
-
- Grassl G, Finlay B. Pathogenesis of enteric Salmonella infections. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2008;24:22. - PubMed
-
- Parry C, Hien TT, Dougan G, White N. J. Farrar, Typhoid fever. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

