An update review of stem cell applications in burns and wound care
- PMID: 23162221
- PMCID: PMC3495372
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.101285
An update review of stem cell applications in burns and wound care
Abstract
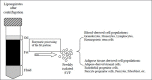
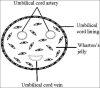
The ultimate goal of the treatment of cutaneous burns and wounds is to restore the damaged skin both structurally and functionally to its original state. Recent research advances have shown the great potential of stem cells in improving the rate and quality of wound healing and regenerating the skin and its appendages. Stem cell-based therapeutic strategies offer new prospects in the medical technology for burns and wounds care. This review seeks to give an updated overview of the applications of stem cell therapy in burns and wound management since our previous review of the "stem cell strategies in burns care".
Keywords: Burns; stem cell; wound.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Burns in the Elderly: Potential Role of Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 29;21(13):4604. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134604. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32610474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue Engineered Skin and Wound Healing: Current Strategies and Future Directions.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(24):3455-3482. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170526094606. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28552069 Review.
-
Epidermal Stem Cells in Skin Wound Healing.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2017 Sep 1;6(9):297-307. doi: 10.1089/wound.2017.0728. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2017. PMID: 28894637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cells and burns: review and therapeutic implications.J Burn Care Res. 2010 Nov-Dec;31(6):874-81. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0b013e3181f9353a. J Burn Care Res. 2010. PMID: 20859216 Review.
-
Stem Cell Therapy: A New Treatment for Burns?Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2011 Oct 21;4(10):1355-1380. doi: 10.3390/ph4101355. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2011. PMID: 27721328 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N-glycosylation profile of undifferentiated and adipogenically differentiated human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: towards a next generation of stem cell markers.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Dec 1;22(23):3100-13. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0108. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23829188 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid creation of skin substitutes from human skin cells and biomimetic nanofibers for acute full-thickness wound repair.Burns. 2015 Dec;41(8):1764-1774. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2015.06.011. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Burns. 2015. PMID: 26187057 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells on the Burn Wound Healing Process.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Feb 11;2019:2340725. doi: 10.1155/2019/2340725. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 30886634 Free PMC article.
-
Alloplastic Epidermal Skin Substitute in the Treatment of Burns.Life (Basel). 2023 Dec 27;14(1):43. doi: 10.3390/life14010043. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38255658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A New Piece in the Puzzle of COVID-19 Treatment.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 3;11:1563. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01563. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32719683 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burd A, Ahmed K, Lam S, Ayyappan T, Huang L. Stem cell strategies in burns care. Burns. 2007;33:282–91. - PubMed
-
- Christiano AM. Epithelial stem cells: Stepping out of their niche. Cell. 2004;118:530–2. - PubMed
-
- Hunt DP, Morris PN, Sterling J, Anderson JA, Joannides A, Jahoda C, et al. A highly enriched niche of precursor cells with neuronal and glial potential within the hair follicle dermal papilla of adult skin. Stem Cells. 2008;26:163–72. - PubMed
-
- Petschnik AE, Klatte JE, Evers LH, Kruse C, Paus R, Danner S. Phenotypic indications that human sweat glands are a rich source of nestin-positive stem cell populations. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:380–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources