Comparison of caudal analgesia between ropivacaine and ropivacaine with clonidine in children: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 23162389
- PMCID: PMC3498654
- DOI: 10.4103/1658-354X.101199
Comparison of caudal analgesia between ropivacaine and ropivacaine with clonidine in children: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Addition of clonidine to ropivacaine (0.2%) can potentially enhance analgesia without producing prolonged motor blockade. The aim of the present study was to compare the post-operative pain relieving quality of ropivacaine 0.2% and clonidine mixture to that of plain ropivacaine 0.2% following caudal administration in children.
Methods: In a prospective, double-blinded, randomized controlled trial, 30 ASA 1 pediatric patients undergoing infraumbilical surgery were randomly allocated to receive a caudal injection of either plain ropivacaine 0.2% (1 ml/kg) (group A) or a mixture of ropivacaine 0.2% (1 ml/kg) with clonidine 2 μg/kg (group B). Objective pain score and need for supplemental analgesics were compared during the 1(st) 24 hours postoperatively. Residual post-operative sedation and motor blockade were also assessed.
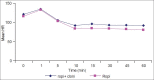
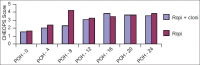
Results: Significantly prolonged duration of post-operative analgesia was observed in group B (P<0.0001). Heart rate and blood pressure were not different in 2 groups. Neither motor blockade nor post-operative sedation varied significantly between the groups.
Conclusion: The combination of clonidine (2 μg/kg) and ropivacaine 0.2% was associated with an improved quality of post-operative analgesia compared to plain 0.2% ropivacaine. The improved analgesic quality of the clonidine-ropivacaine mixture was achieved without causing any significant degree of post-operative sedation or prolongation of motor blockade.
Keywords: Caudal; clonidine; infra-umbilical surgery; paediatrics; ropivacaine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Prospective Double-Blind Comparative Clinical Study Between Caudal Levobupivacaine (0.125%) with Clonidine and Ropivacaine (0.125%) with Clonidine on Post-Operative Analgesia in Paediatric Patients Undergoing Infra-Umbilical Surgery.Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2020 Jul;27(1):52-57. doi: 10.2478/rjaic-2020-0007. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2020. PMID: 34056125 Free PMC article.
-
Ropivacaine-clonidine combination for caudal blockade in children.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2000 Apr;44(4):446-9. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-6576.2000.440415.x. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2000. PMID: 10757579 Clinical Trial.
-
A double-blinded randomized control trial to compare the duration of analgesia using morphine, clonidine, or dexmedetomidine as adjuvants to ropivacaine in caudal anesthesia in children undergoing infraumbilical surgeries.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Jul-Sep;40(3):388-394. doi: 10.4103/joacp.joacp_12_23. Epub 2023 Jul 7. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39391669 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of clonidine as an adjuvant to ropivacaine for caudal analgesia in children undergoing subumbilical surgery.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;28(2):185-9. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.94839. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22557740 Free PMC article.
-
Caudal anesthesia in pediatrics: an update.Minerva Anestesiol. 2006 Jun;72(6):453-9. Minerva Anestesiol. 2006. PMID: 16682915 Review.
Cited by
-
A Prospective Double-Blind Comparative Clinical Study Between Caudal Levobupivacaine (0.125%) with Clonidine and Ropivacaine (0.125%) with Clonidine on Post-Operative Analgesia in Paediatric Patients Undergoing Infra-Umbilical Surgery.Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2020 Jul;27(1):52-57. doi: 10.2478/rjaic-2020-0007. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2020. PMID: 34056125 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of caudally administered clonidine on sevoflurane induced emergence agitation-A randomized trial.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Apr-Jun;38(2):196-200. doi: 10.4103/joacp.JOACP_248_20. Epub 2022 Jun 2. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36171943 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of ropivacaine and bupivacaine with fentanyl for caudal epidural in pediatric surgery.Anesth Essays Res. 2013 May-Aug;7(2):212-5. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.118965. Anesth Essays Res. 2013. PMID: 25885835 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study of Clonidine with Ropivacaine versus Ropivacaine Alone in Epidural Anesthesia for Lower Limb Orthopedic Surgery.Anesth Essays Res. 2017 Oct-Dec;11(4):1035-1039. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_67_17. Anesth Essays Res. 2017. PMID: 29284871 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic Efficacy of Adjuvant Medications in the Pediatric Caudal Block for Infraumbilical Surgery: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Cureus. 2022 Aug 30;14(8):e28582. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28582. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36185831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verghese ST, Hannallah RS. Postoperative pain management in children. Anesthesiol Clin North America. 2005;23:163–84. - PubMed
-
- Habre W, Bergesio R, Johnson C, Hackett P, Joyce D, Sims C, et al. Pharmacokinetics of ropivacaine following caudal analgesia in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2000;10:143–7. - PubMed
-
- Malinovsky JM, Lepage JY, Cosian A, Mussini JM, Pinaudt M, Souron R. Is ketamine or its preservative responsible for neurotoxicity in rabbit? Anesthesiology. 1993;78:101–5. - PubMed
-
- Cook B, Dayle E. The use of additives to local anaesthetic solutions forcaudal epidural blockade. Paediatr Anaesth. 1996;6:353–9. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet F, Boico O, Rostaing S, Loriferne JF, Saada M. Clonidine induced analgesia in post operative patients; epidural versus intramuscular administration. Anesthesiology. 1990;72:423–7. - PubMed

