Connectivity from OR37 expressing olfactory sensory neurons to distinct cell types in the hypothalamus
- PMID: 23162434
- PMCID: PMC3499762
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2012.00084
Connectivity from OR37 expressing olfactory sensory neurons to distinct cell types in the hypothalamus
Abstract
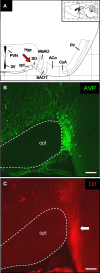
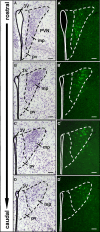
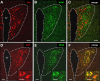
Olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) which express a member from the OR37 subfamily of odorant receptor (OR) genes are wired to the main olfactory bulb (MOB) in a unique monoglomerular fashion; from these glomeruli an untypical connectivity into higher brain centers exists. In the present study we have investigated by DiI and transsynaptic tracing approaches how the connection pattern from these glomeruli into distinct hypothalamic nuclei is organized. The application of DiI onto the ventral domain of the bulb which harbors the OR37 glomeruli resulted in the labeling of fibers within the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and supraoptic nucleus (SO) of the hypothalamus; some of these fibers were covered with varicose-like structures. No DiI-labeled cell somata were detectable in these nuclei. The data indicate that projection neurons which originate in the OR37 region of the MOB form direct connections into these nuclei. The cells that were labeled by the transsynaptic tracer WGA in these nuclei were further characterized. Their distribution pattern in the paraventricular nucleus was reminiscent of cells which produce distinct neuropeptides. Double labeling experiments confirmed that they contained vasopressin, but not the related neuropeptide oxytocin. Morphological analysis revealed that they comprise of magno- and parvocellular cells. A comparative investigation of the WGA-positive cells in the SO demonstrated that these were vasopressin-positive, as well, whereas oxytocin-producing cells of this nucleus also contained no transsynaptic tracer. Together, the data demonstrates a connectivity from OR37 expressing sensory neurons to distinct hypothalamic neurons with the same neuropeptide content.
Keywords: OR37; olfaction; paraventricular nucleus; supraoptic nucleus; vasopressin; wiring.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

