Interleukin-6 modulates colonic transepithelial ion transport in the stress-sensitive wistar kyoto rat
- PMID: 23162465
- PMCID: PMC3491317
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00190
Interleukin-6 modulates colonic transepithelial ion transport in the stress-sensitive wistar kyoto rat
Abstract
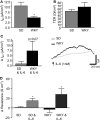
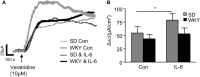
Immunological challenge stimulates secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-6, resulting in variety of biological responses. In the gastrointestinal tract, IL-6 modulates the excitability of submucosal neurons and stimulates secretion into the colonic lumen. When considered in the context of the functional bowel disorder, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), where plasma levels of IL-6 are elevated, this may reflect an important molecular mechanism contributing to symptom flares, particularly in the diarrhea-predominant phenotype. In these studies, colonic ion transport, an indicator of absorption and secretion, was assessed in the stress-sensitive Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rat model of IBS. Mucosa-submucosal colonic preparations from WKY and control Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were mounted in Ussing chambers and the basal short circuit current (I(SC)) was electrophysiologically recorded and compared between the strains. Exposure to IL-6 (1 nM) stimulated a secretory current of greater amplitude in WKY as compared to SD samples. Furthermore, the observed IL-6-mediated potentiation of secretory currents evoked by veratridine and capsaicin in SD rats was blunted in WKY rats. Exposure to IL-6 also stimulated an increase in transepithelial resistance in both SD and WKY colonic tissue. These studies demonstrate that the neuroexcitatory effects of IL-6 on submucosal plexi have functional consequences with alterations in both colonic secretory activity and permeability. The IL-6-induced increase in colonic secretory activity appears to neurally mediated. Thus, local increases in IL-6 levels and subsequent activation of enteric neurons may underlie alterations in absorpto-secretory function in the WKY model of IBS.
Keywords: Wistar Kyoto; capsaicin; electrophysiology; interleukin-6; irritable bowel syndrome; ussing chambers; veratridine.
Figures
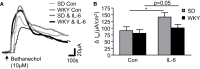

Similar articles
-
Leptin modifies the prosecretory and prokinetic effects of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 on colonic function in Sprague-Dawley rats.Exp Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;101(12):1477-1491. doi: 10.1113/EP085917. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Exp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27676233
-
Altered expression and secretion of colonic interleukin-6 in a stress-sensitive animal model of brain-gut axis dysfunction.J Neuroimmunol. 2011 Jun;235(1-2):48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2011.04.003. Epub 2011 May 11. J Neuroimmunol. 2011. PMID: 21565410
-
Divergent effects of exendin-4 and interleukin-6 on rat colonic secretory and contractile activity are associated with changes in regional vagal afferent signaling.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021 Oct;33(10):e14160. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14160. Epub 2021 May 4. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021. PMID: 33945195
-
Immunomodulation of enteric neural function in irritable bowel syndrome.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 28;21(24):7362-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7362. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26139983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of corticotropin-releasing hormone in irritable bowel syndrome and intestinal inflammation.J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan;42 Suppl 17:48-51. doi: 10.1007/s00535-006-1942-7. J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17238026 Review.
Cited by
-
Mucosal Tuft Cell Density Is Increased in Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome Colonic Biopsies.Front Psychiatry. 2020 May 15;11:436. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00436. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32477197 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of enteric neurons by interleukin-6 and corticotropin-releasing factor contributes to visceral hypersensitivity and altered colonic motility in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome.J Physiol. 2014 Dec 1;592(23):5235-50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.279968. Epub 2014 Sep 25. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25260633 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights which may translate into treatments for irritable bowel syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 31;4:160. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00160. eCollection 2013. Front Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24427135 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor-8 relieves neonatal maternal separation-induced visceral hypersensitivity in rats by regulating expression of TNF-α.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Jan 31;11(2):118. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-6452. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36819583 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of cholinergic and non-cholinergic submucosal neurons along the mouse colon.J Physiol. 2014 Feb 15;592(4):777-93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.265686. Epub 2013 Dec 16. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24344165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiba Y., Guth P. H., Engel E., Nastaskin I., Kaunitz J. D. (1999). Acid-sensing pathways of rat duodenum. Am. J. Physiol. 277, G268–G274 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

