When emotion blinds: a spatiotemporal competition account of emotion-induced blindness
- PMID: 23162497
- PMCID: PMC3491583
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00438
When emotion blinds: a spatiotemporal competition account of emotion-induced blindness
Abstract
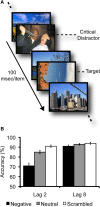
Emotional visual scenes are such powerful attractors of attention that they can disrupt perception of other stimuli that appear soon afterward, an effect known as emotion-induced blindness. What mechanisms underlie this impact of emotion on perception? Evidence suggests that emotion-induced blindness may be distinguishable from closely related phenomena such as the orienting of spatial attention to emotional stimuli or the central resource bottlenecks commonly associated with the attentional blink. Instead, we suggest that emotion-induced blindness reflects relatively early competition between targets and emotional distractors, where spontaneous prioritization of emotional stimuli leads to suppression of competing perceptual representations potentially linked to an overlapping point in time and space.
Keywords: attention; biased competition; emotion; emotion-induced blindness; perception; spatiotemporal competition; visual awareness.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Manipulations of distractor frequency do not mitigate emotion-induced blindness.Cogn Emot. 2019 May;33(3):442-451. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2018.1459490. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Cogn Emot. 2019. PMID: 29644917
-
Dissociating spatial attention and awareness in emotion-induced blindness.Psychol Sci. 2011 Mar;22(3):300-5. doi: 10.1177/0956797610397665. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Psychol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21270446
-
Spatiotemporal competition and task-relevance shape the spatial distribution of emotional interference during rapid visual processing: Evidence from gaze-contingent eye-tracking.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2018 Feb;80(2):426-438. doi: 10.3758/s13414-017-1448-9. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2018. PMID: 29147961 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of emotions on temporal attention.Prog Brain Res. 2017;236:287-309. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Prog Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 29157417 Review.
-
Don't look now! Emotion-induced blindness: The interplay between emotion and attention.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2022 Nov;84(8):2741-2761. doi: 10.3758/s13414-022-02525-z. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2022. PMID: 35701659 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
More than a feeling: The emotional attentional blink relies on non-emotional "pop out," but is weak compared to the attentional blink.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2023 May;85(4):1034-1053. doi: 10.3758/s13414-023-02677-6. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2023. PMID: 36918514 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion-induced blindness reflects competition at early and late processing stages: an ERP study.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2014 Dec;14(4):1485-98. doi: 10.3758/s13415-014-0303-x. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24897955
-
Gaining knowledge mediates changes in perception (without differences in attention): A case for perceptual learning.Behav Brain Sci. 2016 Jan;39:e240. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X15002496. Behav Brain Sci. 2016. PMID: 28355843 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Emotional Information in Banner Blindness.Front Psychol. 2022 May 10;13:813440. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.813440. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35619775 Free PMC article.
-
Current research and emerging directions in emotion-cognition interactions.Front Integr Neurosci. 2014 Nov 11;8:83. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2014.00083. eCollection 2014. Front Integr Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25426034 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

